Radiation modulation of microRNA in prostate cancer cell lines
- PMID: 18668526
- PMCID: PMC3182144
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.20827
Radiation modulation of microRNA in prostate cancer cell lines
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNA) are gene regulators and play an important role in response to cellular stress.
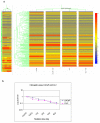
Methods: Using multiplexed quantitative real-time PCR we performed global miRNA screening of prostate cancer cells in response to radiation treatment.
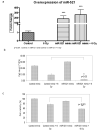
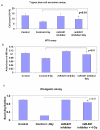
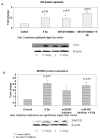
Results: Several miRNA were significantly altered in response to radiation treatment. Significant changes were observed in miR-521 and miR-34c. To determine the role of miR-521 in radiation response we transiently overexpressed miR-521 using miR-521 mimic. The miR-521 mimic significantly sensitized prostate cancer cells to radiation treatment. Conversely, ectopic inhibition of miR-521 resulted in radiation resistance of prostate cancer cells. To determine the mechanism by which miR-521 modulates radiation sensitivity we measured the expression levels of one of its predicted target protein, Cockayne syndrome protein A (CSA). CSA is a DNA repair protein, and its levels correlated inversely with the levels of miR-521. Radiation treatment downregulated the levels of miR-521 and upregulated CSA protein. Similarly, ectopic inhibition of miR-521 resulted in increased CSA protein levels. Therefore by altering the levels of CSA protein, miR-521 sensitized prostate cancer cells to radiation treatment.
Conclusion: miR-521 modulates the expression levels of DNA repair protein, CSA and plays an important role, in the radio-sensitivity of prostate cancer cell lines. Thus miR-521 can be a potential target for enhancing the effect of radiation treatment on prostate cancer cells.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Osada H, Takahashi T. MicroRNAs in biological processes and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28(1):2–12. - PubMed
-
- Marsit CJ, Eddy K, Kelsey KT. MicroRNA responses to cellular stress. Cancer research. 2006;66(22):10843–10848. - PubMed
-
- Yin E, Nelson DO, Coleman MA, Peterson LE, Wyrobek AJ. Gene expression changes in mouse brain after exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation. International journal of radiation biology. 2003;79(10):759–775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

