Molecular ablation of transforming growth factor beta signaling pathways by tyrosine kinase inhibition: the coming of a promising new era in the treatment of tissue fibrosis
- PMID: 18668575
- PMCID: PMC2746747
- DOI: 10.1002/art.23634
Molecular ablation of transforming growth factor beta signaling pathways by tyrosine kinase inhibition: the coming of a promising new era in the treatment of tissue fibrosis
Figures
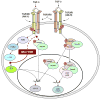
Comment on
-
Treatment of pulmonary fibrosis for twenty weeks with imatinib mesylate in a patient with mixed connective tissue disease.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Aug;58(8):2538-42. doi: 10.1002/art.23694. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18668536
-
Smad1 pathway is activated in systemic sclerosis fibroblasts and is targeted by imatinib mesylate.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Aug;58(8):2528-37. doi: 10.1002/art.23698. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18668566
-
Is imatinib mesylate a promising drug in systemic sclerosis?Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Aug;58(8):2549-52. doi: 10.1002/art.23648. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18668570
-
Imatinib mesylate treatment of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Aug;58(8):2543-8. doi: 10.1002/art.23696. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18668587
References
-
- Jimenez SA, Derk CT. Following the molecular pathways toward and understanding of the pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Ann Int Med. 2004;140:37–50. - PubMed
-
- Gharakee-Kermani M, Phan SH. Molecular mechanisms of and possible treatment strategies for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11:3943–3971. - PubMed
-
- Tskada S, Parson CJ, Rieppe RA. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;364:33–60. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y. Renal fibrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int. 2006;69:213–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

