Multiparameter flow cytometric remission is the most relevant prognostic factor for multiple myeloma patients who undergo autologous stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 18669875
- PMCID: PMC2581991
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-159624
Multiparameter flow cytometric remission is the most relevant prognostic factor for multiple myeloma patients who undergo autologous stem cell transplantation
Abstract
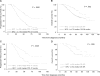
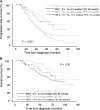
Minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment is standard in many hematologic malignancies but is considered investigational in multiple myeloma (MM). We report a prospective analysis of the prognostic importance of MRD detection by multiparameter flow cytometry (MFC) in 295 newly diagnosed MM patients uniformly treated in the GEM2000 protocol VBMCP/VBAD induction plus autologous stem cell transplantation [ASCT]). MRD status by MFC was determined at day 100 after ASCT. Progression-free survival (PFS; median 71 vs 37 months, P < .001) and overall survival (OS; median not reached vs 89 months, P = .002) were longer in patients who were MRD negative versus MRD positive at day 100 after ASCT. Similar prognostic differentiation was seen in 147 patients who achieved immunofixation-negative complete response after ASCT. Moreover, MRD(-) immunofixation-negative (IFx(-)) patients and MRD(-) IFx(+) patients had significantly longer PFS than MRD(+) IFx(-) patients. Multivariate analysis identified MRD status by MFC at day 100 after ASCT as the most important independent prognostic factor for PFS (HR = 3.64, P = .002) and OS (HR = 2.02, P = .02). Our findings demonstrate the clinical importance of MRD evaluation by MFC, and illustrate the need for further refinement of MM re-sponse criteria. This trial is registered at http://clinicaltrials.gov under identifier NCT00560053.
Figures

Comment in
-
Going with the flow, and beyond, in myeloma.Blood. 2008 Nov 15;112(10):3917-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-08-175026. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18988869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iacobucci I, Saglio G, Rosti G, et al. Achieving a major molecular response at the time of a complete cytogenetic response (CCgR) predicts a better duration of CCgR in imatinib-treated chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:3037–3042. - PubMed
-
- Lo Coco F, Diverio D, Pandolfi PP, et al. Molecular evaluation of residual disease as a predictor of relapse in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Lancet. 1992;340:1437–1438. - PubMed
-
- Vidriales MB, Perez JJ, Lopez-Berges MC, et al. Minimal residual disease in adolescent (older than 14 years) and adult acute lymphoblastic leukemias: early immunophenotypic evaluation has high clinical value. Blood. 2003;101:4695–4700. - PubMed
-
- Corso A, Nozza A, Lazzarino M, et al. Plateau phase in multiple myeloma: an end-point of conventional-dose chemotherapy. Haematologica. 1999;84:336–341. - PubMed
-
- Myeloma Trialists' Collaborative Group. Combination chemotherapy versus melphalan plus prednisone as treatment for multiple myeloma: an overview of 6,633 patients from 27 randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:3832–3842. - PubMed

