Assessing identity, phenotype, and fate of endothelial progenitor cells
- PMID: 18669889
- PMCID: PMC5244813
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.155960
Assessing identity, phenotype, and fate of endothelial progenitor cells
Figures
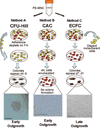



References
-
- Laubichler MD, Aird WC, Maienschein J. The endothelium in history. In: Aird WC, editor. Endothelial Biomedicine. New York: Cambridge University Press; 2007. pp. 5–19.
-
- Aird WC. Introductory essay: The endothelium in health and disease. In: Aird WC, editor. Endothelial Biomedicine. New York: Cambridge University Press; 2007. pp. 1111–1112.
-
- Bouvier CA, Gaynor E, Cintron JR, Bernhardt B, Spaet T. Circulating endothelium as an indication of vascular injury. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1970;40:163–168.
-
- Woywodt A, Blann AD, Kirsch T, Erdbruegger U, Banzet N, Haubitz M, Dignat-George F. Isolation and enumeration of circulating endothelial cells by immunomagnetic isolation: proposal of a definition and a consensus protocol. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:671–677. - PubMed
-
- Schatteman GC, Dunnwald M, Jiao C. Biology of bone marrow-derived endothelial cell precursors. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292:H1–H18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

