Variation of acharan sulfate and monosaccharide composition and analysis of neutral N-glycans in African giant snail (Achatina fulica)
- PMID: 18670878
- PMCID: PMC2630192
- DOI: 10.1007/s10719-008-9149-1
Variation of acharan sulfate and monosaccharide composition and analysis of neutral N-glycans in African giant snail (Achatina fulica)
Abstract
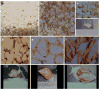
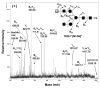
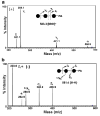
Acharan sulfate content from African giant snail (Achatina fulica) was compared in eggs and snails of different ages. Acharan sulfate was not found in egg. Acharan sulfate disaccharide -->4)-alpha-D-GlcNpAc (1-->4)-alpha-L-IdoAp2S(1-->, analyzed by SAX (strong-anion exchange)-HPLC was observed soon after hatching and increases as the snails grow. Monosaccharide compositional analysis showed that mole % of glucosamine, a major monosaccharide of acharan sulfate, increased with age while mole % of galactose decreased with age. These results suggest that galactans represent a major energy source during development, while acharan sulfate appearing immediately after hatching, is essential for the snail growth. The structures of neutral N-glycans released from eggs by peptide N-glycosidase F (PNGase F), were next elucidated using ESI-MS/MS, MALDI-MS/MS, enzyme digestion, and monosaccharide composition analysis. Three types of neutral N-glycan structures were observed, truncated (Hex(2-4)-HexNAc(2)), high mannose (Hex(5-9)-HexNAc(2)), and complex (Hex(3)-HexNAc(2-10)) types. None showed core fucosylation.
Figures



References
-
- Bishop JR, Schuksz M, Esko JD. Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature. 2007;446:1030–1037. - PubMed
-
- Cantor JO, Nadkarni PP. Hyaluronan: the Jekyll and Hyde molecule. Inflammation and Allergy - Drug Targets. 2006;5:257–260. - PubMed
-
- Volpi N. Advances in Pharmacology. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 2006. Chondroitin sulfate structure, role and pharmacological activity.
-
- Medeiros GF, Mendese A, Castro RAB, Bau EC, Nader HB, Dietrich CP. Distribution of sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the animal kingdom: widespread occurrence of heparin-like compounds in invertebrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1475:287–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

