ORBIT: a multiresolution framework for deformable registration of brain tumor images
- PMID: 18672419
- PMCID: PMC2832332
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2008.916954
ORBIT: a multiresolution framework for deformable registration of brain tumor images
Abstract
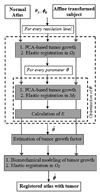
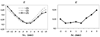
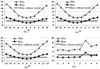
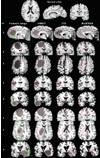
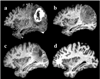
A deformable registration method is proposed for registering a normal brain atlas with images of brain tumor patients. The registration is facilitated by first simulating the tumor mass effect in the normal atlas in order to create an atlas image that is as similar as possible to the patient's image. An optimization framework is used to optimize the location of tumor seed as well as other parameters of the tumor growth model, based on the pattern of deformation around the tumor region. In particular, the optimization is implemented in a multiresolution and hierarchical scheme, and it is accelerated by using a principal component analysis (PCA)-based model of tumor growth and mass effect, trained on a computationally more expensive biomechanical model. Validation on simulated and real images shows that the proposed registration framework, referred to as ORBIT (optimization of tumor parameters and registration of brain images with tumors), outperforms other available registration methods particularly for the regions close to the tumor, and it has the potential to assist in constructing statistical atlases from tumor-diseased brain images.
Figures

References
-
- Miller M, Banerjee A, Christensen G, Joshi S, Khaneja N, Grenander U, Matejic L. Statistical methods in computational anatomy. Statist. Meth. Med. Res. 1997;vol. 6:267–299. - PubMed
-
- Thompson PM, Mega MS, Woods RP, Zoumalan CI, Lindshield CJ, Blanton RE, Moussai J, Holmes CJ, Cummings JL, Toga AW. Cortical change in alzheimer’s disease detected with a disease-specific population-based brain atlas. Cerebral Cortex (Cary) 2001 Jan.vol. 11(no. 1):1–16. 2001. - PubMed
-
- Thompson PM, Giedd JN, Woods RP, MacDonald D, Evans AC, Toga AW. Growth patterns in the developing brain detected by using continuum-mechanical tensor maps. Nature. 2000 Mar.vol. 6774:190–193. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Csernansky JG, Davatzikos C, Fox NC, Frisoni GB, Thompson PM. Computer-assisted imaging to assess brain structure in healthy and diseased brains. Lancet. 2003;vol. 2:79–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

