Tissue microarrays analysis in chondrosarcomas: light microscopy, immunohistochemistry and xenograft study
- PMID: 18673514
- PMCID: PMC2500106
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-3-S1-S25
Tissue microarrays analysis in chondrosarcomas: light microscopy, immunohistochemistry and xenograft study
Abstract
Background: Chondrosarcoma (Chs) is the third most frequent primary malignant tumour of bone and can be primary or secondary, the latter results mainly from the malignant transformation of a benign pre-existing tumour.
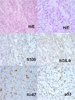
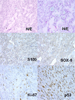
Methods: All the cases diagnosed as Chs (primary tumours, recurrences and/or metastasis and xenotransplanted Chs) from the files of our Department were collected. Only cases with paraffin blocks available were selected (Total 32 cases). Six Tissue Microarrays (TMAs) were performed and all the cases and biopsies were distributed into the following groups: a) only paraffin block available from primary and/or metastatic tumours (3 TMAs), b) paraffin block available from primary and/or metastatic tumours as well as from the corresponding Nude mice xenotransplant (2 TMAs), c) only paraffin block available from xenotransplanted Chs (1 TMA). A reclassification of all the cases was performed; in addition, conventional hematoxylin-eosin as well as immunohistochemistry staining (S100, SOX-9, Ki-67, BCL-2, p53, p16, CK, CD99, Survivin and Caveolin) was analyzed in all the TMA.
Results: The distribution of the cases according to the histopathological pattern and the location of tumours were as follows: fourteen Grade I Chs (all primaries), two primary Grade II Chs, ten Grade III Chs (all primaries), five dedifferentiated Chs (four primaries and one primary with metastasis), and two Chs from cell cultures (Ch grade III). One recurrent extraskeletal myxoid Chs was included as a control in the TMA. Although there was heterogeneity in immunohistochemistry results of the different material analyzed, S100, SOX-9, Caveolin and Survivin were more expressed. The number of passages in xenotransplants fluctuated between 1 and 13. Curiously, in Grade I Chs, these implanted tumours hardly grew, and the number of passages did not exceed one.
Conclusion: The study of Chs by means of TMA techniques is very important because it will improve the assessment of different antibodies applied in the immunohistochemical assays. Xenotransplanted tumours in TMA improve knowledge concerning the variability in the morphological pattern shown by these tumours during the evolution in nudes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A tissue microarray study of osteosarcoma: histopathologic and immunohistochemical validation of xenotransplanted tumors as preclinical models.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2010 Oct;18(5):453-61. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0b013e3181daace3. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2010. PMID: 20436344
-
Tissue microarrays: applications in study of p16 and p53 alterations in Ewing's cell lines.Diagn Pathol. 2008 Jul 15;3 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S27. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-3-S1-S27. Diagn Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18673516 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiles of angiogenesis in two high grade chondrosarcomas: A xenotransplant experience in nude mice.Histol Histopathol. 2017 Dec;32(12):1281-1291. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-880. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Histol Histopathol. 2017. PMID: 28155218
-
[Dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma. A study of 13 clinical cases and review of the literature].Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1994;80(8):669-80. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1994. PMID: 7638395 Review. French.
-
Chondrosarcoma of the jaw bones: a review of 224 cases reported to date and an analysis of prognostic factors.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Apr;48(4):452-460. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2018.11.006. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 30528199 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting survivin as a potential new treatment for chondrosarcoma of bone.Oncogenesis. 2016 May 9;5(5):e222. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2016.33. Oncogenesis. 2016. PMID: 27159675 Free PMC article.
-
High-risk gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) and synovial sarcoma display similar angiogenic profiles: a nude mice xenograft study.Ecancermedicalscience. 2017 Mar 9;11:726. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2017.726. eCollection 2017. Ecancermedicalscience. 2017. PMID: 28386296 Free PMC article.
-
Dedifferentiated Chondrosarcoma: Diagnostic Controversies and Emerging Therapeutic Targets.Curr Oncol Rep. 2023 Oct;25(10):1117-1126. doi: 10.1007/s11912-023-01441-1. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Curr Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37603119 Review.
-
The antiapoptotic gene survivin is highly expressed in human chondrosarcoma and promotes drug resistance in chondrosarcoma cells in vitro.BMC Cancer. 2011 Apr 2;11:120. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-120. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21457573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hassan S, Ferrario C, Mamo A, Basik M. Tissue microarrays: emerging standard for biomarker validation. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2007 - PubMed
-
- Kramer MW, Merseburger AS, Hennenlotter J, Kuczyk M. Tissue microarrays in clinical urology – Technical considerations. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2007. pp. 1–7. - PubMed
-
- Merseburger AS, Kuczyk MA, Serth J, Bokemeyer C, Young DY, Sun L, Connelly RR, McLeod DG, Mostofi FK, Srivastava SK, et al. Limitations of tissue microarrays in the evaluation of focal alterations of bcl-2 and p53 in whole mount derived prostate tissues. Oncol Rep. 2003;10:223–228. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous