Experiences of a long-term randomized controlled prevention trial in a maiden environment: Estonian Postmenopausal Hormone Therapy trial
- PMID: 18673555
- PMCID: PMC2529341
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-8-51
Experiences of a long-term randomized controlled prevention trial in a maiden environment: Estonian Postmenopausal Hormone Therapy trial
Abstract
Background: Preventive drugs require long-term trials to show their effectiveness or harms and often a lot of changes occur during post-marketing studies. The purpose of this article is to describe the research process in a long-term randomized controlled trial and discuss the impact and consequences of changes in the research environment.
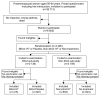
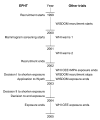
Methods: The Estonian Postmenopausal Hormone Therapy trial (EPHT), originally planned to continue for five years, was planned in co-operation with the Women's International Study of Long-Duration Oestrogen after Menopause (WISDOM) in the UK. In addition to health outcomes, EPHT was specifically designed to study the impact of postmenopausal hormone therapy (HT) on health services utilization.
Results: After EPHT recruited in 1999-2001 the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) in the USA decided to stop the estrogen-progestin trial after a mean of 5.2 years in July 2002 because of increased risk of breast cancer and later in 2004 the estrogen-only trial because HT increased the risk of stroke, decreased the risk of hip fracture, and did not affect coronary heart disease incidence. WISDOM was halted in autumn 2002. These decisions had a major influence on EPHT.
Conclusion: Changes in Estonian society challenged EPHT to find a balance between the needs of achieving responses to the trial aims with a limited budget and simultaneously maintaining the safety of trial participants. Flexibility was the main key for success. Rapid changes are not limited only to transiting societies but are true also in developed countries and the risk must be included in planning all long-term trials. The role of ethical and data monitoring committees in situations with emerging new data from other studies needs specification. Longer funding for preventive trials and more flexibility in budgeting are mandatory. Who should prove the effectiveness of an (old) drug for a new preventive indication? In preventive drug trials companies may donate drugs but they take a financial risk, especially with licensed drugs. Public funding is crucial to avoid commercial biases. Legislation to share the costs of large post-marketing trials as well as regulation of manufacturer's participation is needed. [ISRCTN35338757].
Figures
References
-
- Oakley A. Social support and motherhood. The natural history of a research project. Oxford, Blackwell; 1992.
-
- Oakley A, Strange V, Stephenson J, Forrest S, Monteiro H. Evaluating Processes: A Case Study of a Randomized Controlled Trial of Sex Education. Evaluation. 2004;10:440–462. doi: 10.1177/1356389004050220. - DOI
-
- Oakley A, Rajan L, Grant A. Social support and pregnancy outcome. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1990;97:155–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous