Identification and characterization of novel human tissue-specific RFX transcription factors
- PMID: 18673564
- PMCID: PMC2533330
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-226
Identification and characterization of novel human tissue-specific RFX transcription factors
Abstract
Background: Five regulatory factor X (RFX) transcription factors (TFs)-RFX1-5-have been previously characterized in the human genome, which have been demonstrated to be critical for development and are associated with an expanding list of serious human disease conditions including major histocompatibility (MHC) class II deficiency and ciliaophathies.
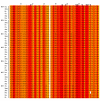
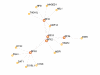
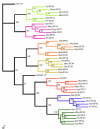
Results: In this study, we have identified two additional RFX genes-RFX6 and RFX7-in the current human genome sequences. Both RFX6 and RFX7 are demonstrated to be winged-helix TFs and have well conserved RFX DNA binding domains (DBDs), which are also found in winged-helix TFs RFX1-5. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that the RFX family in the human genome has undergone at least three gene duplications in evolution and the seven human RFX genes can be clearly categorized into three subgroups: (1) RFX1-3, (2) RFX4 and RFX6, and (3) RFX5 and RFX7. Our functional genomics analysis suggests that RFX6 and RFX7 have distinct expression profiles. RFX6 is expressed almost exclusively in the pancreatic islets, while RFX7 has high ubiquitous expression in nearly all tissues examined, particularly in various brain tissues.
Conclusion: The identification and further characterization of these two novel RFX genes hold promise for gaining critical insight into development and many disease conditions in mammals, potentially leading to identification of disease genes and biomarkers.
Figures
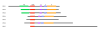
References
-
- Reith W, Satola S, Sanchez CH, Amaldi I, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Griscelli C, Hadam MR, Mach B. Congenital immunodeficiency with a regulatory defect in MHC class II gene expression lacks a specific HLA-DR promoter binding protein, RF-X. Cell. 1988;53:897–906. - PubMed
-
- Kara CJ, Glimcher LH. Regulation of MHC class II gene transcription. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991;3:16–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

