Single cell cytometry of protein function in RNAi treated cells and in native populations
- PMID: 18673568
- PMCID: PMC2529295
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-9-43
Single cell cytometry of protein function in RNAi treated cells and in native populations
Abstract
Background: High Content Screening has been shown to improve results of RNAi and other perturbations, however significant intra-sample heterogeneity is common and can complicate some analyses. Single cell cytometry can extract important information from subpopulations within these samples. Such approaches are important for immune cells analyzed by flow cytometry, but have not been broadly available for adherent cells that are critical to the study of solid-tumor cancers and other disease models.
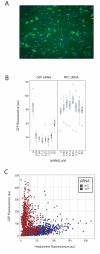
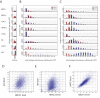
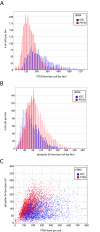
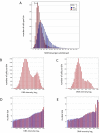
Results: We have directly quantitated the effect of resolving RNAi treatments at the single cell level in experimental systems for both exogenous and endogenous targets. Analyzing the effect of an siRNA that targets GFP at the single cell level permits a stronger measure of the absolute function of the siRNA by gating to eliminate background levels of GFP intensities. Extending these methods to endogenous proteins, we have shown that well-level results of the knockdown of PTEN results in an increase in phospho-S6 levels, but at the single cell level, the correlation reveals the role of other inputs into the pathway. In a third example, reduction of STAT3 levels by siRNA causes an accumulation of cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, but does not induce apoptosis or necrosis when compared to control cells that express the same levels of STAT3. In a final example, the effect of reduced p53 levels on increased adriamycin sensitivity for colon carcinoma cells was demonstrated at the whole-well level using siRNA knockdown and in control and untreated cells at the single cell level.
Conclusion: We find that single cell analysis methods are generally applicable to a wide range of experiments in adherent cells using technology that is becoming increasingly available to most laboratories. It is well-suited to emerging models of signaling dysfunction, such as oncogene addition and oncogenic shock. Single cell cytometry can demonstrate effects on cell function for protein levels that differ by as little as 20%. Biological differences that result from changes in protein level or pathway activation state can be modulated directly by RNAi treatment or extracted from the natural variability intrinsic to cells grown under normal culture conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Hannon GJ. RNAi: A Guide to Gene Silencing. 1. Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA , Cold Spring Harbor Press; 2003. p. 436.
-
- Appasani K. In: RNA Interference Technology: From Basic Science to Drug Development. 1st. Appasani K, editor. Cambridge, UK , Cambridge University Press; 2005. p. 510.
-
- Aza-Blanc P, Cooper CL, Wagner K, Batalov S, Deveraux QL, Cooke MP. Identification of modulators of TRAIL-induced apoptosis via RNAi-based phenotypic screening. Molecular Cell. 2003;12:627–637. - PubMed
-
- Berns K, Hijmans EM, Mullenders J, Brummelkamp TR, Velds A, Heimerikx M, Kerkhoven RM, Madiredjo M, Nijkamp W, Weigelt B, Agami R, Ge W, Cavet G, Linsley PS, Beijersbergen RL, Bernards R. A large-scale RNAi screen in human cells identifies new components of the p53 pathway. Nature. 2004;428:431–437. - PubMed
-
- Downward J. Use of RNA interference libraries to investigate oncogenic signalling in mammalian cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:8376–8383. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

