The prevention of endothelial dysfunction through endothelial cell apoptosis inhibition in a hypercholesterolemic rabbit model: the effect of L-arginine supplementation
- PMID: 18673573
- PMCID: PMC2533308
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-7-27
The prevention of endothelial dysfunction through endothelial cell apoptosis inhibition in a hypercholesterolemic rabbit model: the effect of L-arginine supplementation
Abstract
Background: The impact of L-arginine on atherogenesis and its ability to prevent endothelial dysfunction have been studied extensively during the past years. L-arginine is a substance for nitric oxide synthesis which involves in apoptosis. Hypercholesterolemia promotes endothelial dysfunction, and it is hypothesized that L-arginine prevents endothelial dysfunction through endothelial cells apoptosis inhibition. To test this hypothesis, thirty rabbits were assigned into two groups. The control group received 1% cholesterol diet for 4 weeks, and the L-arginine group received same diets plus 3% L-arginine in drinking water.
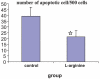
Results: No significant differences were observed in cholesterol level between two groups, but the nitrite concentration in L-arginine group was significantly higher than other group (control group: 11.8 +/- 1; L-arginine group: 14.7 +/- 0.5 micromol/l); (p < 0.05). The aorta score of fatty streak in control group was 0.875 +/- 0.35, but no fatty streak lesion was detected in L-arginine group (p < 0.05). The number of intimal apoptotic cells/500 cells of aorta in two groups of experiment were statistically different (control group: 39.3 +/- 7.6; L-arginine group: 21.5 +/- 5.3) (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The inhibition of endothelial cells apoptosis by L-arginine restores endothelial function in a model of hypercholesterolemia.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

