Cholinergic neurons of mouse intrinsic cardiac ganglia contain noradrenergic enzymes, norepinephrine transporters, and the neurotrophin receptors tropomyosin-related kinase A and p75
- PMID: 18674600
- PMCID: PMC2640831
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.063
Cholinergic neurons of mouse intrinsic cardiac ganglia contain noradrenergic enzymes, norepinephrine transporters, and the neurotrophin receptors tropomyosin-related kinase A and p75
Abstract
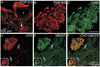
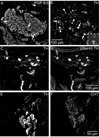
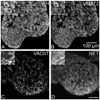
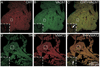
Half of the cholinergic neurons of human and primate intrinsic cardiac ganglia (ICG) have a dual cholinergic/noradrenergic phenotype. Likewise, a large subpopulation of cholinergic neurons of the mouse heart expresses enzymes needed for synthesis of norepinephrine (NE), but they lack the vesicular monoamine transporter type 2 (VMAT2) required for catecholamine storage. In the present study, we determined the full scope of noradrenergic properties (i.e. synthetic enzymes and transporters) expressed by cholinergic neurons of mouse ICG, estimated the relative abundance of neurons expressing different elements of the noradrenergic phenotype, and evaluated the colocalization of cholinergic and noradrenergic markers in atrial nerve fibers. Stellate ganglia were used as a positive control for noradrenergic markers. Using fluorescence immunohistochemistry and confocal microscopy, we found that about 30% of cholinergic cell bodies contained tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), including the activated form that is phosphorylated at Ser-40 (pSer40 TH). Dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH) and norepinephrine transporter (NET) were present in all cholinergic somata, indicating a wider capability for dopamine metabolism and catecholamine uptake. Yet, cholinergic somata lacked VMAT2, precluding the potential for NE storage and vesicular release. In contrast to cholinergic somata, cardiac nerve fibers rarely showed colocalization of cholinergic and noradrenergic markers. Instead, these labels were closely apposed but clearly distinct from each other. Since cholinergic somata expressed several noradrenergic proteins, we questioned whether these neurons might also contain trophic factor receptors typical of noradrenergic neurons. Indeed, we found that all cholinergic cell bodies of mouse ICG, like noradrenergic cell bodies of the stellate ganglia, contained both tropomyosin-related kinase A (TrkA) and p75 neurotrophin receptors. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that mouse intrinsic cardiac neurons (ICNs), like those of humans, have a complex neurochemical phenotype that goes beyond the classical view of cardiac parasympathetic neurons. They also suggest that neurotrophins and local NE synthesis might have important effects on neurons of the mouse ICG.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Localization of multiple neurotransmitters in surgically derived specimens of human atrial ganglia.Neuroscience. 2009 Dec 15;164(3):1170-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.09.001. Epub 2009 Sep 9. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19747529
-
Coexpression of cholinergic and noradrenergic phenotypes in human and nonhuman autonomic nervous system.J Comp Neurol. 2005 Nov 21;492(3):370-9. doi: 10.1002/cne.20745. J Comp Neurol. 2005. PMID: 16217790 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial Infarction Causes Transient Cholinergic Transdifferentiation of Cardiac Sympathetic Nerves via gp130.J Neurosci. 2016 Jan 13;36(2):479-88. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3556-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26758839 Free PMC article.
-
Human phenotypes and animal knockout models of genetic autonomic disorders.J Biomed Sci. 2004 Jan-Feb;11(1):4-10. doi: 10.1007/BF02256543. J Biomed Sci. 2004. PMID: 14730204 Review.
-
Characterization of the intrinsic cardiac nervous system.Auton Neurosci. 2016 Aug;199:3-16. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2016.08.006. Epub 2016 Aug 6. Auton Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27568996 Review.
Cited by
-
Untangling Peripheral Sympathetic Neurocircuits.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Feb 10;9:842656. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.842656. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35224065 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of peripheral neural circuits that regulate heart rate using optogenetic and viral vector strategies.Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 26;10(1):1944. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09770-1. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31028266 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of gp130 in dopamine beta-hydroxylase-expressing neurons leads to autonomic imbalance and increased reperfusion arrhythmias.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Sep;297(3):H960-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00409.2009. Epub 2009 Jul 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19592611 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical characterization of the intrinsic cardiac neural plexus in whole-mount mouse heart preparations.Heart Rhythm. 2011 May;8(5):731-8. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2011.01.013. Epub 2011 Jan 11. Heart Rhythm. 2011. PMID: 21232628 Free PMC article.
-
Altered atrial neurotransmitter release in transgenic p75(-/-) and gp130 KO mice.Neurosci Lett. 2012 Oct 31;529(1):55-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.08.089. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Neurosci Lett. 2012. PMID: 22999927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams DJ, Cuevas J. Electrophysiological properties of intrinisc cardiac neurons. In: Armour JA, Ardell JL, editors. Basic and Clinical Neurocardiology. New York: Oxford University Press; 2004. pp. 1–60.
-
- Airaksinen MS, Saarma M. The GDNF family: signaling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;5:383–394. - PubMed
-
- Al J, Epstein PN, Gozal D, Yang B, Wurster R, Cheng ZJ. Morphology and topography of nucleus ambiguus projections to cardiac ganglia in rats and mice. Neuroscience. 2007;149:845–860. - PubMed
-
- Ardell JL. Structure and function of mammalian intrinsic cardiac neurons. In: Armour JA, Ardell JL, editors. Neurocardiology. New York: Oxford University Press; 1994. pp. 95–114.
-
- Ardell JL. Intrathoracic neuronal regulation of cardiac function. In: Armour JA, Ardell JL, editors. Basic and Clinical Neurocardiology. New York: Oxford University Press; 2004. pp. 118–152.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

