CD4+/CD8+ T cell ratio for diagnosis of HIV-1 infection in infants: Women and Infants Transmission Study
- PMID: 18676551
- PMCID: PMC4699439
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2007-2308
CD4+/CD8+ T cell ratio for diagnosis of HIV-1 infection in infants: Women and Infants Transmission Study
Abstract
Objective: In this study, we tested the hypothesis that the CD4(+)/CD8(+) T cell ratio could predict HIV infection status in HIV-exposed infants.
Methods: CD4(+)/CD8(+) T cell ratios were determined from data for live-born singleton infants who had been prospectively enrolled in the Women and Infants Transmission Study. Data for 2208 infants with known HIV infection status (179 HIV-infected and 2029 uninfected infants) were analyzed.
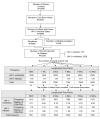
Results: Receiver operating characteristic curves indicated that the CD4(+)/CD8(+) T cell ratio performed better than the proportion of CD4(+) T cells for diagnosis of HIV infection as early as 2 months of age, and this relationship was unaffected by adjustment for maternal race/ethnicity, infant birth weight, gestational age, and gender. At 4 months of age, 90% specificity for HIV diagnosis was associated with 60% sensitivity. For ease of use, graphical estimates based on cubic splines for the time-dependent parameters in a Box-Cox transformation (L), the median (M), and the coefficient of variation (S) were used to create LMS centile curves to show the sensitivity and specificity of CD4(+)/CD8(+) T cell ratios in HIV-infected and uninfected infants until 12 months of age. At 6 months of age, a simplified equation that incorporated sequential CD4(+)/CD8(+) T cell ratios and hematocrit values resulted in improved receiver operating characteristic curves, with 94% positive predictive value and 98% negative predictive value. The positive and negative predictive values remained above 90% in simulated infant populations over a wide range of HIV infection prevalence values.
Conclusions: In the absence of virological diagnosis, a presumptive diagnosis of HIV infection status can be made on the basis of CD4(+)/CD8(+) T cell ratios in HIV-1-exposed infants after 2 months of age; sensitivity and specificity can be improved at 6 months by using a discriminant analysis equation.
Figures





References
-
- Read JS. Prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV. In: Zeichner SL, Read JS, editors. Textbook of Pediatric HIV Care. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, England: 2005. pp. 111–133.
-
- Coovadia HM, Rollins NC, Bland RM, et al. Mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 infection during exclusive breastfeeding in the first 6 months of life: an intervention cohort study. Lancet. 2007 Mar 31;369:1107–1116. - PubMed
-
- Little K, Newell ML, Luo C, Ngongo N, Borja MC, McDermott P. Estimating the number of vertically HIV-infected children eligible for antiretroviral treatment in resource-limited settings. Int J Epidemiol. 2007;36:679–87. - PubMed
-
- Paintsil E, Andiman WA. Care and management of the infant of the HIV-1-infected mother. Semin Perinatol. 2007;31:112–123. - PubMed
-
- Little K, Thorne C, Luo C, et al. Disease progression in children with vertically-acquired HIV infection in sub-Saharan Africa: reviewing the need for HIV treatment. Curr HIV Res. 2007;5:139–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- M01 RR000188/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD036117/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI073961/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034841/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 034841/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI050274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GCRC RR000645/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA 015053/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 RR000188/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA015054/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI085339/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 050274-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000645/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA 015054/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD 041983/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 034858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GCRC RR000188/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA015053/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD 036117/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD041983/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

