Encoding NF-kappaB temporal control in response to TNF: distinct roles for the negative regulators IkappaBalpha and A20
- PMID: 18676814
- PMCID: PMC2492747
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1680708
Encoding NF-kappaB temporal control in response to TNF: distinct roles for the negative regulators IkappaBalpha and A20
Abstract
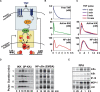
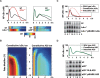
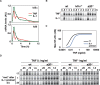
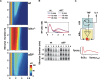
TNF-induced NF-kappaB activity shows complex temporal regulation whose different phases lead to distinct gene expression programs. Combining experimental studies and mathematical modeling, we identify two temporal amplification steps-one determined by the obligate negative feedback regulator IkappaBalpha-that define the duration of the first phase of NF-kappaB activity. The second phase is defined by A20, whose inducible expression provides for a rheostat function by which other inflammatory stimuli can regulate TNF responses. Our results delineate the nonredundant functions implied by the knockout phenotypes of ikappabalpha and a20, and identify the latter as a signaling cross-talk mediator controlling inflammatory and developmental responses.
Figures
References
-
- Aggarwal B.B., Shishodia S., Ashikawa K., Bharti A.C. The role of TNF and its family members in inflammation and cancer: Lessons from gene deletion. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy. 2002;1:327–341. - PubMed
-
- Banner D.W., D’Arcy A., Janes W., Gentz R., Schoenfeld H.J., Broger C., Loetscher H., Lesslauer W. Crystal structure of the soluble human 55 kd TNF receptor-human TNF β complex: Implications for TNF receptor activation. Cell. 1993;73:431–445. - PubMed
-
- Beg A.A., Sha W.C., Bronson R.T., Baltimore D. Constitutive NF-κ B activation, enhanced granulopoiesis, and neonatal lethality in I κ B α-deficient mice. Genes & Dev. 1995;9:2736–2746. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B.A., Milsark I.W., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: Production, distribution, and metabolic fate in vivo. J. Immunol. 1985;135:3972–3977. - PubMed
-
- Boone D.L., Turer E.E., Lee E.G., Ahmad R.C., Wheeler M.T., Tsui C., Hurley P., Chien M., Chai S., Hitotsumatsu O., et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat. Immunol. 2004;5:1052–1060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
