MUC1 oncoprotein blocks death receptor-mediated apoptosis by inhibiting recruitment of caspase-8
- PMID: 18676836
- PMCID: PMC2536759
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0464
MUC1 oncoprotein blocks death receptor-mediated apoptosis by inhibiting recruitment of caspase-8
Abstract
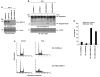
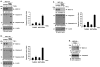
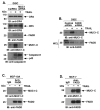
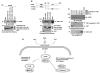
Stimulation of the death receptor superfamily induces the activation of caspase-8 and thereby the apoptotic response. The MUC1 oncoprotein is aberrantly overexpressed by diverse human malignancies and inhibits stress-induced apoptosis. The present results show that MUC1 blocks activation of caspase-8 and apoptosis in the response of malignant cells to tumor necrosis factor alpha, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, and Fas ligand. The results show that MUC1 associates constitutively with caspase-8. The MUC1 cytoplasmic domain (MUC1-CD) binds directly to the caspase-8 p18 fragment upstream to the catalytic Cys(360) site. The results also show that MUC1-CD binds to Fas-associated death domain (FADD) at the death effector domain. In nonmalignant epithelial cells, MUC1 interacts with caspase-8 and FADD as an induced response to death receptor stimulation. The functional significance of these interactions is supported by the demonstration that MUC1 competes with caspase-8 for binding to FADD and blocks recruitment of caspase-8 to the death-inducing signaling complex. These findings indicate that MUC1 is of importance to the physiologic regulation of caspase-8 activity and that overexpression of MUC1, as found in human malignancies, could contribute to constitutive inhibition of death receptor signaling pathways.
Figures


References
-
- Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science. 1998;281:1305–8. - PubMed
-
- Micheau O, Tschopp J. Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell. 2003;114:181–90. - PubMed
-
- Schneider-Brachert W, Tchikov V, Neumeyer J, et al. Compartmentalization of TNF receptor 1 signaling: internalized TNF receptosomes as death signaling vesicles. Immunity. 2004;21:415–28. - PubMed
-
- Boldin M, Goncharov T, Goltsev Y, Wallach D. Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1- and TNF receptor-induced cell-death. Cell. 1996;85:803–15. - PubMed
-
- Muzio M, Chinnaiyan AM, Kischkel FC, et al. FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death-inducing signaling complex. Cell. 1996;85:817–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

