Loss of cannabinoid receptor 1 accelerates intestinal tumor growth
- PMID: 18676872
- PMCID: PMC2561258
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0896
Loss of cannabinoid receptor 1 accelerates intestinal tumor growth
Abstract
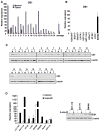
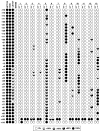
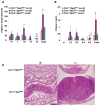
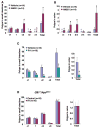
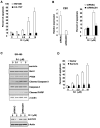
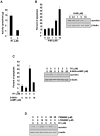
Although endocannabinoid signaling is important for certain aspects of gastrointestinal homeostasis, the role of the cannabinoid receptors (CB) in colorectal cancer has not been defined. Here we show that CB1 expression was silenced in human colorectal cancer due to methylation of the CB1 promoter. Our genetic and pharmacologic studies reveal that loss or inhibition of CB1 accelerated intestinal adenoma growth in Apc(Min/+) mice whereas activation of CB1 attenuated intestinal tumor growth by inducing cell death via down-regulation of the antiapoptotic factor survivin. This down-regulation of survivin by CB1 is mediated by a cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A signaling pathway. These results indicate that the endogenous cannabinoid system may represent a potential therapeutic target for prevention or treatment of colorectal cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Tcf4-GFP reporter mouse model for monitoring effects of Apc mutations during intestinal tumorigenesis.Mol Carcinog. 2009 Sep;48(9):821-31. doi: 10.1002/mc.20526. Mol Carcinog. 2009. PMID: 19263440 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of cannabinoid CB1 receptor and associated signaling networks in brains of cocaine addicts and cocaine-treated rodents.Neuroscience. 2013 Sep 5;247:294-308. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.05.035. Epub 2013 May 29. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23727505
-
The cannabinoid receptor CB1 contributes to the development of ectopic lesions in a mouse model of endometriosis.Hum Reprod. 2017 Jan;32(1):175-184. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew281. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 27821707
-
Regulation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the central nervous system by chronic cannabinoids.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2003;15(2):91-119. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v15.i2.10. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 14977366 Review.
-
Defining key concepts of intestinal and epithelial cancer biology through the use of mouse models.Carcinogenesis. 2017 Oct 1;38(10):953-965. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgx080. Carcinogenesis. 2017. PMID: 28981588 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation between Olive Oil Intake and Gut Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer Prevention.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 10;14(18):3749. doi: 10.3390/nu14183749. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36145125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Cannabis and Cannabinoids for Treatment of Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 20;14(20):5142. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205142. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Insights into Epigenetics and Cannabinoid Receptors.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 26;12(11):1560. doi: 10.3390/biom12111560. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabidiol Combination Enhances Photodynamic Therapy Effects on MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells.Cells. 2024 Jan 18;13(2):187. doi: 10.3390/cells13020187. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38247877 Free PMC article.
-
Energetic metabolism and human sperm motility: impact of CB₁ receptor activation.Endocrinology. 2010 Dec;151(12):5882-92. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0484. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20962050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hall W, Christie M, Currow D. Cannabinoids and cancer: causation, remediation, and palliation. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:35–42. - PubMed
-
- Walsh D, Nelson KA, Mahmoud FA. Established and potential therapeutic applications of cannabinoids in oncology. Support Care Cancer. 2003;11:137–43. - PubMed
-
- Massa F, Monory K. Endocannabinoids and the gastrointestinal tract. J Endocrinol Invest. 2006;29:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Guzman M. Cannabinoids: potential anticancer agents. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:745–55. - PubMed
-
- Patsos HA, Hicks DJ, Greenhough A, Williams AC, Paraskeva C. Cannabinoids and cancer: potential for colorectal cancer therapy. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005;33:712–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37-DA06668/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HD012304/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37-DK-47297/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK-58404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK047297/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37-HD12304/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA-77839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-62112/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA077839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA006668/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062112/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

