In vivo pharmacodynamics of ceftobiprole against multiple bacterial pathogens in murine thigh and lung infection models
- PMID: 18676887
- PMCID: PMC2565885
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01273-07
In vivo pharmacodynamics of ceftobiprole against multiple bacterial pathogens in murine thigh and lung infection models
Abstract
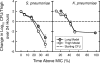
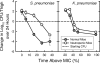
Ceftobiprole medocaril is the parenteral prodrug of ceftobiprole, a novel pyrrolidinone broad-spectrum cephalosporin with in vitro and in vivo bactericidal activities against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae (PRSP). We have used murine thigh and lung infection models in neutropenic and normal mice to characterize the in vivo pharmacokinetic (PK)-pharmacodynamic (PD) activities of ceftobiprole against multiple strains of S. aureus (including MRSA), S. pneumoniae (including PRSP), and gram-negative bacilli. Serum levels of ceftobiprole following the administration of multiple doses were determined by a microbiological assay. In vivo bactericidal activities and postantibiotic effects (PAEs) of ceftobiprole against MRSA and PRSP strains were determined from serial CFU/thigh values following single doses of ceftobiprole (40 and 160 mg/kg of body weight). Dose fractionation studies were used to determine which PK-PD index correlated best with activity. Magnitudes of the PK-PD indices were calculated from MICs and PK parameters. A sigmoid dose-response model was used to estimate the dose (mg/kg/24 h) required to achieve a static and 2-log(10) kill effects over 24 h. PK results showed area under the concentration-time curve/dose values of 1.8 to 2.8 and half-lives of 0.29 to 0.51 h. MICs ranged from 0.015 to 2 microg/ml. Ceftobiprole demonstrated time-dependent killing; its in vivo PAEs varied from 3.8 h to 4.8 h for MRSA and from 0 to 0.8 h for PRSP. The time above MIC (T > MIC) correlated best with efficacy for both MRSA and PRSP. The T > MIC values required for the static doses were significantly longer (P < 0.001) for Enterobacteriaceae (36 to 45%) than for S. aureus (14 to 28%) and S. pneumoniae (15 to 22%). The drug showed activities in the lung model similar to those in the thigh model. The presence of neutrophils significantly enhanced the activity of ceftobiprole against S. pneumoniae but only slightly against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Based on its PD profile, ceftobiprole is a promising new beta-lactam agent with activity against gram-negative and gram-positive organisms including MRSA and PRSP.
Figures



References
-
- AAALAC. 2006, posting date. Guide to the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. AAALAC, Frederick, MD. http://www.aaalac.org.
-
- Andes, D., and W. A. Craig. 2006. Pharmacodynamics of a new cephalosporin, PPI-0903 (TAK-599), active against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in murine thigh and lung infection models: identification of an in vivo pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic target. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50:1376-1383. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

