Antagonistic effect of rifampin on the efficacy of high-dose levofloxacin in staphylococcal experimental foreign-body infection
- PMID: 18676888
- PMCID: PMC2565888
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00458-08
Antagonistic effect of rifampin on the efficacy of high-dose levofloxacin in staphylococcal experimental foreign-body infection
Abstract
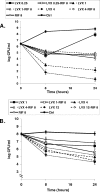
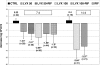
Since levofloxacin at high doses was more active than levofloxacin at conventional doses and was the best therapy alone in a rat model of staphylococcal foreign-body infection, in this study we tested how these differences affect the activities of their respective combinations with rifampin in vitro and in vivo. In vitro studies were performed in the log and stationary phases. By using this model, rifampin at 25 mg/kg of body weight/12 h, levofloxacin at 100 mg/kg/day, levofloxacin at 100 mg/kg/day plus rifampin, levofloxacin at 50 mg/kg/day, levofloxacin at 50 mg/kg/day plus rifampin, or a control treatment was administered for 7 days; and therapy with for levofloxacin at 100 mg/kg/day alone and rifampin alone was prolonged to 14 days. We screened for the appearance of resistant strains. Killing curves in the log phase showed a clear antagonism with levofloxacin at concentrations >or=2x MIC and rifampin and tended to occur in the stationary phase. At the end of 7 days of therapy, levofloxacin at 100 mg/kg/day was the best treatment and decreased the bacterial counts from tissue cage fluid (P < 0.05 compared with the results for groups except those receiving rifampin alone). At the end of 14 days of therapy with levofloxacin at 100 mg/kg/day, levofloxacin at 100 mg/kg/day plus rifampin, and the control treatment, the bacterial counts on the coverslips were 2.24 (P < 0.05 compared with the results with the combined therapy), 3.36, and 5.4 log CFU/ml, respectively. No rifampin or levofloxacin resistance was detected in any group except that receiving rifampin alone. In conclusion, high-dose levofloxacin was the best treatment and no resistant strains appeared; the addition of rifampin showed an antagonistic effect. The efficacy of the rifampin-levofloxacin combination is not significantly improved by the dosage of levofloxacin.
Figures
References
-
- Bahl, D., D. A. Miller, I. Leviton, P. Gialanella, M. J. Wolin, W. Liu, R. Perkins, and M. H. Miller. 1997. In vitro activities of ciprofloxacin and rifampin alone and in combination against growing and nongrowing strains of methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41:1293-1297. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barberan, J., L. Aguilar, G. Carroquino, M. J. Gimenez, B. Sanchez, D. Martinez, and J. Prieto. 2006. Conservative treatment of staphylococcal prosthetic joint infections in elderly patients. Am. J. Med. 119:993.e7-993.e10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

