Subcellular curvature at the perimeter of micropatterned cells influences lamellipodial distribution and cell polarity
- PMID: 18677773
- PMCID: PMC2652852
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.20305
Subcellular curvature at the perimeter of micropatterned cells influences lamellipodial distribution and cell polarity
Abstract
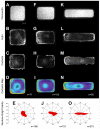
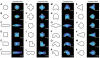
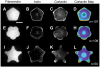
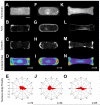
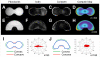
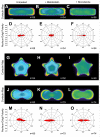
This paper employs substrates that are patterned with shapes having well-defined geometric cues to characterize the influence of curvature on the polarization of highly metastatic B16F10 rat melanoma cells. Substrates were patterned using microcontact printing to define adhesive islands of defined shape and size on a background that otherwise prevents cell adhesion. Cells adherent to these surfaces responded to local curvature at the perimeter of the adhesive islands; convex features promoted the assembly of lamellipodia and concave features promoted the assembly of stress filaments. Cells adherent to rectangular shapes displayed a polarized cytoskeleton that increased with the aspect ratio of the shapes. Shapes that combined local geometric cues, by way of concave or convex edges, with aspect ratio were used to understand the additive effects of shape on polarization. The dependence of cell polarity on shape was determined in the presence of small molecules that alter actomyosin contractility and revealed a stronger dependence on contractility for shapes having straight edges, in contrast to those having curved edges. This study demonstrates that the cytoskeleton modulates cell polarity in response to multiple geometric cues in the extracellular environment.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
References
-
- Ballestrem C, Wehrle-Haller B, Imhof BA. Actin dynamics in living mammalian cells. J Cell Sci. 1998;111(Pt 12):1649–58. - PubMed
-
- Brock A, Chang E, Ho CC, LeDuc P, Jiang X, Whitesides GM, Ingber DE. Geometric determinants of directional cell motility revealed using microcontact printing. Langmuir. 2003;19(5):1611–7. - PubMed
-
- Charest PG, Firtel RA. Feedback signaling controls leading-edge formation during chemotaxis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006;16(4):339–47. - PubMed
-
- Chen CS, Alonso JL, Ostuni E, Whitesides GM, Ingber DE. Cell shape provides global control of focal adhesion assembly. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;307(2):355–61. - PubMed
-
- Chen CS, Mrksich M, Huang S, Whitesides GM, Ingber DE. Geometric control of cell life and death. Science. 1997;276(5317):1425–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources