Maternally inherited Birk Barel mental retardation dysmorphism syndrome caused by a mutation in the genomically imprinted potassium channel KCNK9
- PMID: 18678320
- PMCID: PMC2495061
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.07.010
Maternally inherited Birk Barel mental retardation dysmorphism syndrome caused by a mutation in the genomically imprinted potassium channel KCNK9
Abstract
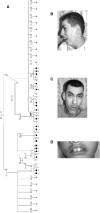
We describe a maternally transmitted genomic-imprinting syndrome of mental retardation, hypotonia, and unique dysmorphism with elongated face. We mapped the disease-associated locus to approximately 7.27 Mb on chromosome 8q24 and demonstrated that the disease is caused by a missense mutation in the maternal copy of KCNK9 within this locus. KCNK9 is maternally transmitted (imprinted with paternal silencing) and encodes K(2P)9.1, a member of the two pore-domain potassium channel (K(2P)) subfamily. The mutation fully abolishes the channel's currents--both when functioning as a homodimer or as a heterodimer with K(2P)3.1.
Figures

References
-
- Temple I.K. Imprinting in human disease with special reference to transient neonatal diabetes and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Endocr. Dev. 2007;12:113–123. - PubMed
-
- Harel T., Goldberg Y., Shalev S.A., Chervinski I., Ofir R., Birk O.S. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2I: Phenotypic variability within a large consanguineous Bedouin family associated with a novel FKRP mutation. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2004;12:38–43. - PubMed
-
- Fishelson M., Geiger D. Exact genetic linkage computations for general pedigrees. Bioinformatics. 2002;18:S189–S198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

