Oxidative stress regulates adipocyte apolipoprotein e and suppresses its expression in obesity
- PMID: 18678613
- PMCID: PMC2570395
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-0592
Oxidative stress regulates adipocyte apolipoprotein e and suppresses its expression in obesity
Abstract
Objective: Endogenous expression of apolipoprotein E (apoE) has a significant impact on adipocyte lipid metabolism and is markedly suppressed in obesity. Adipose tissue oxidant stress is emerging as an important mediator of adipocyte dysfunction. These studies were undertaken to evaluate the role of oxidant stress for regulation of adipocyte apoE.
Research design and methods: ApoE gene and protein expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes or mature adipocytes and adipose tissue from C57/BL6 mice was evaluated after induction of oxidant stress. The response of adipose tissue and adipocytes from obese compared with lean mice to antioxidants was also assessed.
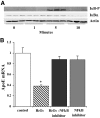
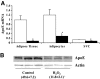
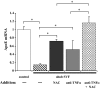
Results: Oxidant stress in 3T3-L1 cells or adipocytes and adipose tissue from lean mice significantly reduced apoE mRNA and protein level. Inclusion of an antioxidant eliminated this reduction. Oxidant stress was accompanied by activation of the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) transcription complex, and its effect on apoE was eliminated by an NF-kappaB activation inhibitor. Treatment of freshly isolated adipose tissue or mature adipocytes from obese mice with antioxidant increased apoE expression but had no effect on cells or tissue from lean mice. Incubation of freshly isolated adipocytes from lean mice with stromovascular cells from obese mice significantly suppressed adipocyte apoE compared with incubation with stromovascular cells from lean mice, but this suppression was reversed by inclusion of antioxidant or a neutralizing antibody to tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
Conclusions: Oxidant stress significantly modulates adipose tissue and adipocyte apoE expression. Furthermore, oxidant stress contributes to suppression of adipocyte apoE in obesity. This suppression depends on interaction between adipose tissue stromovascular cells and adipocytes.
Figures
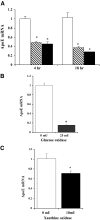
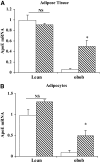
 , 0.5 mmol/l; ▪, 1.0 mmol/l. Adipocytes were treated with or without 25 mU/ml glucose oxidase (B) or 10 mU/ml xanthine oxidase (C) with 0.6 mmol/l hypoxanthine for 18 h in serum-free medium. Total RNA was extracted and apoE mRNA level was measured using RT-PCR. Each experiment was performed using triplicate samples and was repeated three times with similar results. Results shown are from a representative experiment as means ± SD. *P < 0.001 for the difference compared with untreated control.
, 0.5 mmol/l; ▪, 1.0 mmol/l. Adipocytes were treated with or without 25 mU/ml glucose oxidase (B) or 10 mU/ml xanthine oxidase (C) with 0.6 mmol/l hypoxanthine for 18 h in serum-free medium. Total RNA was extracted and apoE mRNA level was measured using RT-PCR. Each experiment was performed using triplicate samples and was repeated three times with similar results. Results shown are from a representative experiment as means ± SD. *P < 0.001 for the difference compared with untreated control.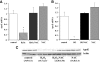
 , NAC. *P < 0.0005 for comparison of untreated vs. NAC treated.
, NAC. *P < 0.0005 for comparison of untreated vs. NAC treated.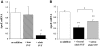
Similar articles
-
Hyperglycemia and advanced glycosylation end products suppress adipocyte apoE expression: implications for adipocyte triglyceride metabolism.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Oct;299(4):E615-23. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00273.2010. Epub 2010 Jul 20. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20647555 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated suppression of adipocyte apolipoprotein E gene transcription: primary role for the nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB pathway and NFkappaB p50.Endocrinology. 2008 Aug;149(8):4051-8. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0340. Epub 2008 May 8. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18467438 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II regulates adipocyte apolipoprotein E expression.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Nov;92(11):4366-72. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-1592. Epub 2007 Sep 4. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17785354
-
Insights into the roles of Apolipoprotein E in adipocyte biology and obesity.Int J Obes (Lond). 2024 Sep;48(9):1205-1215. doi: 10.1038/s41366-024-01549-9. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Int J Obes (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38839985 Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E synthesized by adipocyte and apolipoprotein E carried on lipoproteins modulate adipocyte triglyceride content.Lipids Health Dis. 2014 Aug 23;13:136. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-13-136. Lipids Health Dis. 2014. PMID: 25148848 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adipose tissue: friend or foe?Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012 Dec;9(12):689-702. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2012.148. Epub 2012 Nov 13. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 23149834 Review.
-
Expression of the human apoE2 isoform in adipocytes: altered cellular processing and impaired adipocyte lipogenesis.J Lipid Res. 2011 Sep;52(9):1733-41. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M017160. Epub 2011 Jul 8. J Lipid Res. 2011. PMID: 21743035 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism for endogenously expressed ApoE modulation of adipocyte very low density lipoprotein metabolism: role in endocytic and lipase-mediated metabolic pathways.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 13;284(46):31512-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.004754. Epub 2009 Sep 18. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19767394 Free PMC article.
-
Biobreeding rat islets exhibit reduced antioxidative defense and N-acetyl cysteine treatment delays type 1 diabetes.J Endocrinol. 2013 Jan 18;216(2):111-23. doi: 10.1530/JOE-12-0385. Print 2013 Feb. J Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23111281 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression deregulation by KRAS G12D and G12V in a BRAF V600E context.Mol Cancer. 2008 Dec 16;7:92. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-7-92. Mol Cancer. 2008. PMID: 19087308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fantuzzi G, Mazzone T: Adipose tissue and atherosclerosis: exploring the connection. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27: 996–1003, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Haffner SM: Relationship of metabolic risk factors and development of cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Obesity 14 (Suppl. 3): 121S–127S, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Berg AH, Scherer PE: Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 96: 939–949, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Lumeng CN, DeYoung SM, Bodzin JL, et al.: Increased inflammatory properties of adipose tissue macrophages recruited during diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 56: 16–23, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

