Puumala hantavirus excretion kinetics in bank voles (Myodes glareolus)
- PMID: 18680643
- PMCID: PMC2600398
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1408.080221
Puumala hantavirus excretion kinetics in bank voles (Myodes glareolus)
Abstract
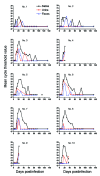
Puumala hantavirus is present in bank voles (Myodes glareolus) and is believed to be spread mainly by contaminated excretions. In this study, we subcutaneously inoculated 10 bank voles with Puumala virus and sampled excretions until day 133 postinfection. Levels of shed viral RNA peaked within 11-28, 14-21, and 11-28 days postinfection for saliva, urine, and feces, respectively. The latest detection of viral RNA was 84, 44, and 44 days postinfection in saliva, urine, and feces, respectively. In contrast, blood of 5 of 6 animals contained viral RNA at day 133 postinfection, suggesting that bank voles secrete virus only during a limited time of the infection. Intranasal inoculations with bank vole saliva, urine, or feces were all infectious for virus-negative bank voles, indicating that these 3 transmission routes may occur in nature and that rodent saliva might play a role in transmission to humans.
Figures

References
-
- Lee H. The Bunyaviridae. In: Elliott R, editor. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. New York: Plenum Press; 1996. p. 253–67.
-
- The Swedish Institute for Infectious Disease Control. Statistics for nephropathia epidemica [cited 2008 May 14]. Available from http://www.smittskyddsinstitutet.se/statistik/sorkfeber
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
