A simple-shear rheometer for linear viscoelastic characterization of vocal fold tissues at phonatory frequencies
- PMID: 18681608
- PMCID: PMC2561277
- DOI: 10.1121/1.2946715
A simple-shear rheometer for linear viscoelastic characterization of vocal fold tissues at phonatory frequencies
Abstract
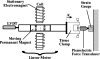
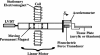
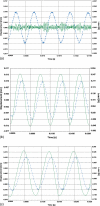
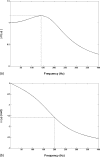
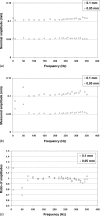
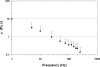
Previous studies reporting the linear viscoelastic shear properties of the human vocal fold cover or mucosa have been based on torsional rheometry, with measurements limited to low audio frequencies, up to around 80 Hz. This paper describes the design and validation of a custom-built, controlled-strain, linear, simple-shear rheometer system capable of direct empirical measurements of viscoelastic shear properties at phonatory frequencies. A tissue specimen was subjected to simple shear between two parallel, rigid acrylic plates, with a linear motor creating a translational sinusoidal displacement of the specimen via the upper plate, and the lower plate transmitting the harmonic shear force resulting from the viscoelastic response of the specimen. The displacement of the specimen was measured by a linear variable differential transformer whereas the shear force was detected by a piezoelectric transducer. The frequency response characteristics of these system components were assessed by vibration experiments with accelerometers. Measurements of the viscoelastic shear moduli (G' and G") of a standard ANSI S2.21 polyurethane material and those of human vocal fold cover specimens were made, along with estimation of the system signal and noise levels. Preliminary results showed that the rheometer can provide valid and reliable rheometric data of vocal fold lamina propria specimens at frequencies of up to around 250 Hz, well into the phonatory range.
Figures








References
-
- American National Standards Institute, Inc. (1998). “Method for preparation of a standard material for dynamic mechanical measurements,” ANSI S2.21-1998 (Acoustical Society of America, New York, NY: ).
-
- Barnes, H. A., Hutton, J. F., and Walters, K. (1989). An Introduction to Rheology (Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands: ).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

