SIRT1 confers protection against UVB- and H2O2-induced cell death via modulation of p53 and JNK in cultured skin keratinocytes
- PMID: 18681908
- PMCID: PMC4516512
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00453.x
SIRT1 confers protection against UVB- and H2O2-induced cell death via modulation of p53 and JNK in cultured skin keratinocytes
Abstract
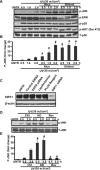
SIRT1 is a member of a highly conserved gene family (sirtuins) encoding nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)(+)-dependent deacetylases, originally found to deacetylate histones leading to increased DNA stability and prolonged survival in yeast and higher organisms, including mammals. SIRT1 has been found to function as a deacetylase for numerous protein targets involved in various cellular pathways, including stress responses, apoptosis and axonal degeneration. However, the role of SIRT1 in ultraviolet (UV) signalling pathways remains unknown. Using cell culture and Western blot analysis in this study we found that SIRT1 is expressed in cultured human skin keratinocytes. Both UV radiation and H(2)O(2), two major inducers of skin cell damage, down-regulate SIRT1 in a time- and dose-dependent manner. We observed that reactive oxygen species-mediated JNK activation is involved in this SIRT1 down-regulation. SIRT1 activator, resveratrol, which has been considered as an important antioxidant, protects against UV- and H(2)O(2)-induced cell death, whereas SIRT inhibitors such as sirtinol and nicotinamide enhance cell death. Activation of SIRT1 negatively regulates UV- and H(2)O(2)-induced p53 acetylation, because nicotinamide and sirtinol as well as SIRT1 siRNA enhance UV- and H(2)O(2)-induced p53 acetylation, whereas SIRT1 activator resveratrol inhibits it. We also found that SIRT1 is involved in UV-induced AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and downstream acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), phosphofructose kinase-2 (PFK-2) phosphorylation. Collectively, our data provide new insights into understanding of the molecular mechanisms of UV-induced skin aging, suggesting that SIRT1 activators such as resveratrol could serve as new anti-skin aging agents.
Figures





References
-
- Vaziri H, Dessain SK, Ng Eaton E, et al. hSIR2(SIRT1) functions as an NAD-dependent p53 deacetylase. Cell. 2001;107:149–59. - PubMed
-
- Luo J, Nikolaev AY, Imai S, et al. Negative control of p53 by Sir2alpha promotes cell survival under stress. Cell. 2001;107:137–48. - PubMed
-
- Bouras T, Fu M, Sauve AA, et al. SIRT1 deacetylation and repression of p300 involves lysine residues 1020/1024 within the cell cycle regulatory domain 1. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:10264–76. - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, et al. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell. 1999;96:857–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

