Maintenance of large subpopulations of differentiated CD8 T-cells two years after cytomegalovirus infection in Gambian infants
- PMID: 18682836
- PMCID: PMC2483415
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002905
Maintenance of large subpopulations of differentiated CD8 T-cells two years after cytomegalovirus infection in Gambian infants
Abstract
Background: In a previously published study, we found that large differentiated subpopulations of CD8 T-cells emerged rapidly after CMV infection in young infants and persisted throughout the following year. Here we describe a follow-up study conducted on the same infants to establish whether the differentiated subpopulations continued through the second year post-infection.
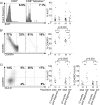
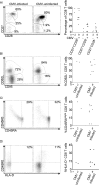
Methodology / principal findings: CMV-specific cells identified using tetramers remained more activated and differentiated than the overall CD8 population. The large subpopulation of differentiated cytotoxic (CD28(-)CD62L(-)Bcl-2(low)CD95(+)perforin(+)) cells that emerged rapidly after infection remained stable after two years. No similar subpopulation was found in CMV-uninfected infants indicating that two years after infection, CMV remained a major factor in driving CD8 T-cell differentiation. Although markers of activation (CD45R0 and HLA-D) declined throughout the first year, HLA-D expression continued to decline during the second year and CD45R0 expression increased slightly. The age-related increase in IFNgamma response observed during the first year continued but was non-significant during the second year, indicating that the rate of functional improvement had slowed substantially. CONCLUSIONS / SIGNIFICANCE: The large differentiated subpopulations of CD8 T-cells that had emerged immediately after CMV infection persisted through the second year post-infection, while levels of activation and functional capacity remained fairly constant.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Pass RF. Epidemiology and transmission of cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1985;152:243–248. - PubMed
-
- Gamadia L, Remmerswaal E, Weel J, Bemelman F, van Lier R, et al. Primary immune responses to human CMV: a critical role for IFN-γ-producing CD4+ T cells in protection against CMV disease. Blood. 2003;101:2686–2692. - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Tu W-W, Sharp M, Tongson E, He X-S, et al. Antiviral CD8 T cells in the control of primary human cytomegalovirus infection in early childhood. J Infect Dis. 2004;189:1619–1627. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

