Olfactory learning in the rat neonate soon after birth
- PMID: 18683189
- PMCID: PMC2574692
- DOI: 10.1002/dev.20318
Olfactory learning in the rat neonate soon after birth
Abstract
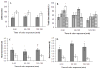
The first hours of a newborn rat's life entail locating and attaching to the mother's nipple not only for nutrition but also for protection and warmth. The present study sought to characterize olfactory learning in the rat neonate immediately after birth. Newborn rats were exposed to an odor at various time periods soon after birth and tested for behavioral activation and attachment to a surrogate nipple in the presence of this odor at 4-5 hr postpartum. Regardless of when pups were presented the odor (0, 1, or 2 hr after birth) motor activity was greater among pups previously exposed to the odor than pups with no odor experience. Similarly, latency to attach to the nipple in the presence of the odor was lower among odor-preexposed pups, especially when odor exposure began within an hour of cesarean delivery. Odor exposure immediately after birth for just 15 min was sufficient to increase motor activity and to decrease latency to attach to a similarly scented surrogate nipple. These results suggest that olfactory experience very soon after birth can shape subsequent olfactory responses. The relative importance of the dearth of postnatal experience or of elevated neurochemicals immediately after birth and possible associative mechanisms underlying this learning is discussed.
(c) 2008 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
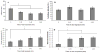
Similar articles
-
Olfactory learning in the rat immediately after birth: Unique salience of first odors.Dev Psychobiol. 2009 Sep;51(6):488-504. doi: 10.1002/dev.20388. Dev Psychobiol. 2009. PMID: 19582793 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal activation of alcohol-related prenatal memories: impact on the first suckling response.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002 Oct;26(10):1512-22. doi: 10.1097/01.ALC.0000034668.93601.8F. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002. PMID: 12394284
-
Mere odor exposure learning in the rat neonate immediately after birth and 1 day later.Dev Psychobiol. 2010 May;52(4):343-51. doi: 10.1002/dev.20456. Dev Psychobiol. 2010. PMID: 20411590 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between perinatal and neonatal associative learning defined by contiguous olfactory and tactile stimulation.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1999 May;71(3):272-88. doi: 10.1006/nlme.1998.3882. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1999. PMID: 10196106
-
Fetal alcohol syndrome: early olfactory learning as a model system to study neurobehavioral deficits.Int J Neurosci. 1997 Jan;89(1-2):119-32. doi: 10.3109/00207459708988467. Int J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9134450 Review.
Cited by
-
Early life trauma and attachment: immediate and enduring effects on neurobehavioral and stress axis development.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Mar 21;5:33. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00033. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 24711804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exposure to maternal odor enhances intake of a taste that mimicks the sensory attributes of ethanol.Learn Behav. 2019 Dec;47(4):302-309. doi: 10.3758/s13420-019-00373-w. Learn Behav. 2019. PMID: 31264146
-
Early development of olfactory circuit function.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Jul 26;17:1225186. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1225186. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37565031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olfactory learning in the rat immediately after birth: Unique salience of first odors.Dev Psychobiol. 2009 Sep;51(6):488-504. doi: 10.1002/dev.20388. Dev Psychobiol. 2009. PMID: 19582793 Free PMC article.
-
RNA profiles of rat olfactory epithelia: individual and age related variations.BMC Genomics. 2009 Dec 2;10:572. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-572. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19954510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel RA, Ronca AE, Alberts JR. Perinatal stimulation facilitates suckling onset in newborn rats. Developmental Psychobiology. 1998;32:91–99. - PubMed
-
- Alberts JR, May B. Nonnutritive, thermotactile induction of filial huddling in rat pups. Developmental Psychobiology. 1984;17:161–181. - PubMed
-
- Andrew RJ, Clifton PG, Gibbs ME. Enhancement of effectiveness of learning by testosterone in domestic chicks. Journal of Comparative Physiology and Psychology. 1981;95:406–417. - PubMed
-
- Bacher LF, Robertson SS, Smotherman WP. An intrinsic source of behavioral regulation that influences discrete responses to cues important for the initiation of suckling. Behavioral Neuroscience. 2000;114:594–601. - PubMed
-
- Bordner KA, Molina JC, Spear NE. 2007. Operant conditioning supported by ethanol reinforcement in the newborn rat. Manuscript submitted for publication.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

