Cadherins and catenins at synapses: roles in synaptogenesis and synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 18684518
- PMCID: PMC2623250
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.07.001
Cadherins and catenins at synapses: roles in synaptogenesis and synaptic plasticity
Abstract
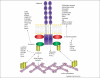
Synapse formation involves reciprocal interactions between cells resulting in formation of a structure optimized for efficient information transfer. Recent work has implicated constituents of the cadherin-catenin cell-adhesion complex in both synapse formation and plasticity. In this review, we describe recent interesting discoveries on mechanisms of cadherin complex function, in addition to regulating adhesion, that are relevant for understanding the role of this complex in synaptogenesis and plasticity. We describe how this complex acts via (i) recruitment/stabilization of intracellular partners; (ii) regulation of intracellular signaling pathways; (iii) regulation of cadherin surface levels, stability and turnover; (iv) stabilization of receptors; and (v) regulation of gene expression. These exciting discoveries provide insights into novel functional roles of the complex beyond regulating cell adhesion.
Figures

References
-
- Yuste R, Bonhoeffer T. Morphological changes in dendritic spines associated with long-term synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001;24:1071–1089. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez VA, Sabatini BL. Anatomical and physiological plasticity of dendritic spines. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2007;30:79–97. - PubMed
-
- Bourne J, Harris KM. Do thin spines learn to be mushroom spines that remember? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2007;17:381–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

