An intronic microRNA silences genes that are functionally antagonistic to its host gene
- PMID: 18684991
- PMCID: PMC2532712
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn513
An intronic microRNA silences genes that are functionally antagonistic to its host gene
Abstract
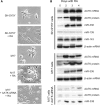
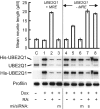
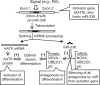
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short noncoding RNAs that down-regulate gene expression by silencing specific target mRNAs. While many miRNAs are transcribed from their own genes, nearly half map within introns of 'host' genes, the significance of which remains unclear. We report that transcriptional activation of apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase (AATK), essential for neuronal differentiation, also generates miR-338 from an AATK gene intron that silences a family of mRNAs whose protein products are negative regulators of neuronal differentiation. We conclude that an intronic miRNA, transcribed together with the host gene mRNA, may serve the interest of its host gene by silencing a cohort of genes that are functionally antagonistic to the host gene itself.
Figures



References
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates C. elegans developmental timing. Nature. 2000;403:901–906. - PubMed
-
- Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science. 2001;294:853–858. - PubMed
-
- Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:858–862. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Ambros V. An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:862–864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

