Effect of tiotropium on health-related quality of life as a primary efficacy endpoint in COPD
- PMID: 18686739
- PMCID: PMC2629970
- DOI: 10.2147/copd.s2463
Effect of tiotropium on health-related quality of life as a primary efficacy endpoint in COPD
Abstract
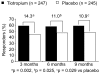
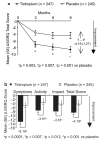
Clinical manifestations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including airflow limitation, dyspnea, and activity limitation, ultimately lead to impaired health-related quality of life (HRQoL). This 9-month, randomized, double-blind, multicenter study compared the effect of once-daily tiotropium 18 microg and placebo on HRQoL, spirometric parameters, and exacerbations in 554 patients with moderate-to-severe COPD. HRQoL was assessed using the St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) and the new 8-item Visual Simplified Respiratory Questionnaire (VSRQ), which is currently being validated. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a reduction of at least 4 units in the SGRQ total score at study end (Month 9). Mean +/- SD baseline SGRQ total score was 47.4 +/- 18.1. Significantly more tiotropium-treated patients achieved a reduction of at least 4 units in the SGRQ score vs placebo at study end (59.1% vs 48.2%, respectively; p = 0.029). Tiotropium significantly improved spirometric parameters (forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1]: 0.11 +/- 0.02 L vs 0.01 +/- 0.02 L; between-group difference: 0.10 +/- 0.03 L, p = 0.0001) and reduced exacerbations vs placebo. Maintenance treatment with tiotropium provided significant and clinically relevant improvements in HRQoL, as measured by the SGRQ.
Figures
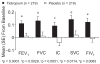
References
-
- American Thoracic Society. Standards for the diagnosis and care of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152(5 Pt 2):S77–121. - PubMed
-
- Bourbeau J, Maltais F, Rouleau M, et al. French-Canadian version of the Chronic Respiratory and St George’s Respiratory questionnaires: an assessment of their psychometric properties in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Can Respir J. 2004;11:480–6. - PubMed
-
- Casaburi R, Mahler DA, Jones PW, et al. A long-term evaluation of once-daily inhaled tiotropium in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2002;19:217–24. - PubMed
-
- Celli B, ZuWallack R, Wang S, et al. Improvement in resting inspiratory capacity and hyperinflation with tiotropium in COPD patients with increased static lung volumes. Chest. 2003;124:1743–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

