Influence of early antioxidant supplements on clinical evolution and organ function in critically ill cardiac surgery, major trauma, and subarachnoid hemorrhage patients
- PMID: 18687132
- PMCID: PMC2575590
- DOI: 10.1186/cc6981
Influence of early antioxidant supplements on clinical evolution and organ function in critically ill cardiac surgery, major trauma, and subarachnoid hemorrhage patients
Abstract
Introduction: Oxidative stress is involved in the development of secondary tissue damage and organ failure. Micronutrients contributing to the antioxidant (AOX) defense exhibit low plasma levels during critical illness. The aim of this study was to investigate the impact of early AOX micronutrients on clinical outcome in intensive care unit (ICU) patients with conditions characterized by oxidative stress.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-center trial in patients admitted to a university hospital ICU with organ failure after complicated cardiac surgery, major trauma, or subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stratification by diagnosis was performed before randomization. The intervention was intravenous supplements for 5 days (selenium 270 microg, zinc 30 mg, vitamin C 1.1 g, and vitamin B1 100 mg) with a double-loading dose on days 1 and 2 or placebo.
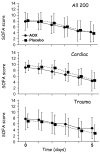
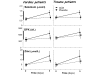
Results: Two hundred patients were included (102 AOX and 98 placebo). While age and gender did not differ, brain injury was more severe in the AOX trauma group (P = 0.019). Organ function endpoints did not differ: incidence of acute kidney failure and sequential organ failure assessment score decrease were similar (-3.2 +/- 3.2 versus -4.2 +/- 2.3 over the course of 5 days). Plasma concentrations of selenium, zinc, and glutathione peroxidase, low on admission, increased significantly to within normal values in the AOX group. C-reactive protein decreased faster in the AOX group (P = 0.039). Infectious complications did not differ. Length of hospital stay did not differ (16.5 versus 20 days), being shorter only in surviving AOX trauma patients (-10 days; P = 0.045).
Conclusion: The AOX intervention did not reduce early organ dysfunction but significantly reduced the inflammatory response in cardiac surgery and trauma patients, which may prove beneficial in conditions with an intense inflammation.
Trials registration: Clinical Trials.gov RCT Register: NCT00515736.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

