Endothelial function in human immunodeficiency virus-infected antiretroviral-naive subjects before and after starting potent antiretroviral therapy: The ACTG (AIDS Clinical Trials Group) Study 5152s
- PMID: 18687253
- PMCID: PMC2603599
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.04.049
Endothelial function in human immunodeficiency virus-infected antiretroviral-naive subjects before and after starting potent antiretroviral therapy: The ACTG (AIDS Clinical Trials Group) Study 5152s
Abstract
Objectives: This study evaluated the effects of 3 class-sparing antiretroviral therapy (ART) regimens on endothelial function in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected subjects participating in a randomized trial.
Background: Endothelial dysfunction has been observed in patients receiving ART for HIV infection.
Methods: This was a prospective, multicenter study of treatment-naive subjects who were randomly assigned to receive a protease inhibitor-sparing regimen of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) + efavirenz, a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-sparing regimen of NRTIs + lopinavir/ritonavir, or a NRTI-sparing regimen of efavirenz + lopinavir/ritonavir. The NRTIs were lamivudine + stavudine, zidovudine, or tenofovir. Brachial artery flow-mediated dilation (FMD) was determined by B-mode ultrasound before starting on ART, then after 4 and 24 weeks.
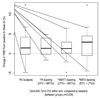
Results: There were 82 subjects (median age 35 years, 91% men, 54% white). Baseline CD4 cell counts and plasma HIV ribonucleic acid (RNA) values were 245 cells/mm(3) and 4.8 log(10) copies/ml, respectively. At baseline, FMD was 3.68% (interquartile range [IQR] 1.98% to 5.51%). After 4 and 24 weeks of ART, plasma HIV RNA decreased by 2.1 and 3.0 log(10) copies/ml, respectively. FMD increased by 0.74% (IQR -0.62% to +2.74%, p = 0.003) and 1.48% (IQR -0.20% to +4.30%, p < 0.001), respectively, with similar changes in each arm (Kruskal-Wallis p value >0.600). The decrease in plasma HIV RNA at 24 weeks was associated with greater FMD (r(s) = -0.30, p = 0.017).
Conclusions: Among treatment-naive individuals with HIV, 3 different ART regimens rapidly improved endothelial function. Benefits were similar for all ART regimens, appeared quickly, and persisted at 24 weeks.
Conflict of interest statement
Francesca J. Torriani, MD – Advisory Board: Abbott
Lauren Komarow, MS – None
Robert A. Parker, ScD – None
Bruno R. Cotter, MD – None
Judith S. Currier, MD
Research Grants: Merck and Co. – Raltegravir in Lipodystrophy, Tibotec – Antiretroviral Treatment Study, GSK – Antiretroviral Treatment, Theratechnologies (3) – Lipodystrophy, Schering-Plough – Antiretroviral Treatment
Honoraria: Gilead – DSMB, Koronnis – DSMB, Achillion – DSMB, Vertex
Consultant/Advisory Board: Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Merck, Gilead
Michael P. Dube, MD
Research Grants: Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb
Consultant: Glaxo Smith Kline, Tibotec, Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbott
Carl J. Fichtenbaum, MD
Research Grants: Abbott Research Grant – unrestricted study immune reconstitution
Abbott and Bristol-Myers Squibb – grants to support CME program
Speakers’ Bureau: Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead
Honoraria: Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead
Mariana Gerschenson, PhD - None
Carol Mitchell, PhD - none
Robert L. Murphy, MD
Research Grant: Bristol-Myers Squibb - Antiretroviral therapy and endothelial function
Consultant/Advisory Board: Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb
Kathleen E. Squires, MD
Research Grant: Bristol-Myers Squibb – grant is held by Thomas Jefferson University
Honoraria: Gilead Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbott
Advisory Board: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Abbott
James H. Stein, MD
Research Grant: Bristol-Myers Squibb – Antiretroviral therapy and endothelial function
Consultant: Abbott – DSMB for lipid trial, development of vitamin D analogue
Figures
References
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Friis-Moller N, Reiss P, Sabin CA, et al. Class of antiretroviral drugs and the risk of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1723–1735. - PubMed
-
- Obel N, Thomsen HF, Kronborg G, et al. Ischemic heart disease in HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected individuals: a population-based cohort study. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:1625–1631. - PubMed
-
- Deanfield JE, Halcox JP, Rabelink TJ. Endothelial function and dysfunction: testing and clinical relevance. Circulation. 2007;115:1285–1295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI38558/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MD000173/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR00075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR16176/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RR00750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI025859/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR016467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MD000173/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL072711/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI56933/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI056933/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI34853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 RR016176/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI025915/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI25915/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR16467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI38855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI25859/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL72711/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI69432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials