Yeast linker histone Hho1p is required for efficient RNA polymerase I processivity and transcriptional silencing at the ribosomal DNA
- PMID: 18687885
- PMCID: PMC2575252
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0709403105
Yeast linker histone Hho1p is required for efficient RNA polymerase I processivity and transcriptional silencing at the ribosomal DNA
Abstract
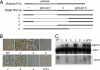
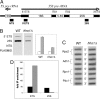
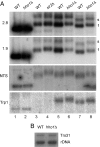
Nucleosome core particles in eukaryotes are linked by a stretch of DNA that is usually associated with a linker histone. Here, we show in yeast, that the presence of yeast linker histone Hho1p represses expression of a pol II transcribed gene (MET15) embedded in the rDNA. In vivo deletions of Hho1p sequences showed that the second globular domain is sufficient for that repression, whereas the presence of the N terminus is required for its derepression. In contrast, a run-on assay confirmed by a ChIP experiment showed that Hho1p is required for maximal pol I processivity during rDNA transcription. Psoralen accessibility experiments indicated that Hho1p is necessary for normal rDNA compaction. DNA array expression analysis comparing RNA transcripts in wild-type and hho1 strains before and after a heat-shock showed that Hho1p is necessary to achieve wild-type mRNA levels of transcripts that encode ribosomal components. Taken together, our results suggest that Hho1p is involved in rDNA compaction, and like core histones, is required for efficient rDNA transcription by pol I.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Woodcock CL, Skoultchi AI, Fan Y. Role of linker histone in chromatin structure and function: H1 stoichiometry and nucleosome repeat length. Chromosome Res. 2006;14:17–25. - PubMed
-
- Simpson RT. Structure of the chromatosome, a chromatin particle containing 160 base pairs of DNA and all the histones. Biochemistry. 1978;17:5524–5531. - PubMed
-
- Kasinsky HE, Lewis JD, Dacks JB, Ausió J. Origin of H1 linker histones. FASEB J. 2001;15:34–42. - PubMed
-
- Cerf C, et al. Homo- and heteronuclear two-dimensional NMR studies of the globular domain of histone H1: Full assignment, tertiary structure, and comparison with the globular domain of histone H5. Biochemistry. 1994;33:11079–11086. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

