The kinase domain of mitochondrial PINK1 faces the cytoplasm
- PMID: 18687899
- PMCID: PMC2575334
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0802814105
The kinase domain of mitochondrial PINK1 faces the cytoplasm
Abstract
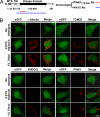
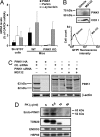
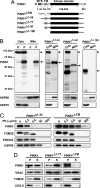
Mutations in PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1) are a cause of autosomal recessive familial Parkinson's disease (PD). Efforts in deducing the PINK1 signaling pathway have been hindered by controversy around its subcellular and submitochondrial localization and the authenticity of its reported substrates. We show here that this mitochondrial protein exhibits a topology in which the kinase domain faces the cytoplasm and the N-terminal tail is inside the mitochondria. Although deletion of the transmembrane domain disrupts this topology, common PD-linked PINK1 mutations do not. These results are critical in rectifying the location and orientation of PINK1 in mitochondria, and they should help decipher its normal physiological function and potential pathogenic role in PD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Vila M, Przedborski S. Genetic clues to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Nat Med. 2004;10(Suppl):S58–S62. - PubMed
-
- Klein C, Lohmann-Hedrich K. Impact of recent genetic findings in Parkinson's disease. Curr Opin Neurol. 2007;20:453–464. - PubMed
-
- Valente EM, et al. Hereditary early-onset Parkinson's disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science. 2004;304:1158–1160. - PubMed
-
- Deng H, Jankovic J, Guo Y, Xie W, Le W. Small interfering RNA targeting the PINK1 induces apoptosis in dopaminergic cells SH-SY5Y. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;337:1133–1138. - PubMed
-
- Petit A, et al. Wild-type PINK1 prevents basal and induced neuronal apoptosis, a protective effect abrogated by Parkinson disease-related mutations. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:34025–34032. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS11766/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021617/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058056/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK58056/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES013177/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- AG21617/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- A608702/PHS HHS/United States
- P01 NS011766/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS042269/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS42269/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS038370/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HD83062/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NS38370/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- ES013177/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

