Deletional tolerance mediated by extrathymic Aire-expressing cells
- PMID: 18687966
- PMCID: PMC2532844
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1159407
Deletional tolerance mediated by extrathymic Aire-expressing cells
Abstract
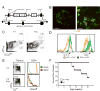
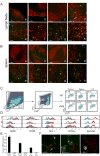
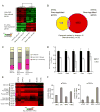
The prevention of autoimmunity requires the elimination of self-reactive T cells during their development and maturation. The expression of diverse self-antigens by stromal cells in the thymus is essential to this process and depends, in part, on the activity of the autoimmune regulator (Aire) gene. Here we report the identification of extrathymic Aire-expressing cells (eTACs) resident within the secondary lymphoid organs. These stromally derived eTACs express a diverse array of distinct self-antigens and are capable of interacting with and deleting naïve autoreactive T cells. Using two-photon microscopy, we observed stable antigen-specific interactions between eTACs and autoreactive T cells. We propose that such a secondary network of self-antigen-expressing stromal cells may help reinforce immune tolerance by preventing the maturation of autoreactive T cells that escape thymic negative selection.
Figures

Comment in
-
Immunology. A breath of Aire for the periphery.Science. 2008 Aug 8;321(5890):776-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1162966. Science. 2008. PMID: 18687943 No abstract available.
References
-
- Smith KM, Olson DC, Hirose R, Hanahan D. Int Immunol. 1997;9:1355. - PubMed
-
- Derbinski J, Schulte A, Kyewski B, Klein L. Nature Immunol. 2001;2:1032. - PubMed
-
- Anderson MS, et al. Science. 2002;298:1395. - PubMed
-
- Liston A, Lesage S, Wilson J, Peltonen L, Goodnow CC. Nature Immunol. 2003;4:350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

