The role of Dickkopf-1 in bone development, homeostasis, and disease
- PMID: 18687985
- PMCID: PMC2628360
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-145169
The role of Dickkopf-1 in bone development, homeostasis, and disease
Abstract
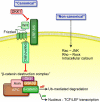
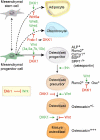
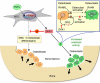
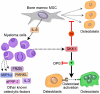
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is central to bone development and homeostasis in adulthood and its deregulation is associated with bone pathologies. Dickkopf-1 (DKK1), a soluble inhibitor of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling required for embryonic head development, regulates Wnt signaling by binding to the Wnt coreceptor lipoprotein-related protein-5 (LRP5)/Arrow. LRP5 mutations causing high bone mass syndromes disrupt DKK1-mediated regulation of LRP5. Forced overexpression of Dkk1 in osteoblasts causes osteopenia, disruption of the hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) niche, and defects in HSC function. Dkk1 also inhibits fracture repair. Studies suggest that DKK1 activation in osteoblasts is the underlying cause of glucocorticoid- and estrogen deficiency-mediated osteoporosis, and at least partially underlies the teratogenic effects of thalidomide on limb development. DKK1 induces proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in vitro and may play a role in the development of high-grade undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcomas derived from MSC and osteosarcomas. DKK1 has been implicated in causing erosive arthritis, the osteolytic phenotypes of multiple myeloma and metastatic breast cancer, and osteoblastic metastases of prostate cancer. Preclinical studies have shown that neutralizing DKK1/Dkk1 and/or enhancing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling may prove effective in treating bone pathologies. Here, we review the rapidly growing body of literature defining a pivotal role for DKK1 in bone health and disease.
Figures
References
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–480. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto H, Sakane H, Yamamoto H, Michiue T, Kikuchi A. Wnt3a and Dkk1 regulate distinct internalization pathways of LRP6 to tune the activation of beta-catenin signaling. Dev Cell. 2008;15:37–48. - PubMed
-
- Glinka A, Wu W, Delius H, Monaghan AP, Blumenstock C, Niehrs C. Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction. Nature. 1998;391:357–362. - PubMed
-
- Mao B, Wu W, Davidson G, et al. Kremen proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Nature. 2002;417:664–667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

