Endometrial-peritoneal interactions during endometriotic lesion establishment
- PMID: 18688027
- PMCID: PMC2527068
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.071128
Endometrial-peritoneal interactions during endometriotic lesion establishment
Abstract
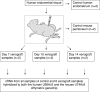
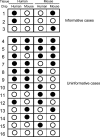
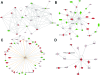
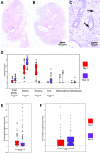
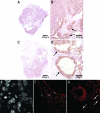
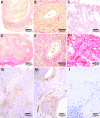
The pathophysiology of endometriosis remains unclear but involves a complex interaction between ectopic endometrium and host peritoneal tissues. We hypothesized that disruption of this interaction would suppress endometriotic lesion formation. We hoped to delineate the molecular and cellular dialogue between ectopic human endometrium and peritoneal tissues in nude mice as a first step toward testing this hypothesis. Human endometrium was xenografted into nude mice, and the resulting lesions were analyzed using microarrays. A novel technique was developed that unambiguously determined whether RNA transcripts identified via microarray analyses originated from human cells (endometrium) or mouse cells (mesothelium). Four key pathways (ubiquitin/proteasome, inflammation, tissue remodeling/repair, and ras-mediated oncogenesis) were revealed, demonstrating communication between host mesothelial cells and ectopic endometrium. Morphometric analysis of nude mouse lesions confirmed that necrosis, inflammation, healing and repair, and cell proliferation occurred during xenograft development. These processes were entirely consistent with the molecular networks revealed by the microarray data. The transcripts detected in the xenografts overlapped with differentially expressed transcripts in a comparison between paired eutopic and ectopic endometria from human endometriotic patients. For the first time, components of the interaction between ectopic endometrium and peritoneal stromal tissues are revealed. Targeted disruption of this dialogue is likely to inhibit endometriotic tissue formation and may prove to be an effective therapeutic strategy for endometriosis.
Figures

References
-
- Strathy JH, Molgaard CA, Coulam CB, Melton LJ., 3rd Endometriosis and infertility: a laparoscopic study of endometriosis among fertile and infertile women. Fertil Steril. 1982;38:667–672. - PubMed
-
- Giudice LC, Kao LC. Endometriosis. Lancet. 2004;364:1789–1799. - PubMed
-
- Sampson JA. Peritoneal endometriosis due to menstrual dissemination of endometrial tissue into the peritoneal cavity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1927;14:442–469.
-
- Bulun SE, Yang S, Fang Z, Gurates B, Tamura M, Sebastian S. Estrogen production and metabolism in endometriosis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002;955:75–85. - PubMed
-
- Ho HN, Wu MY, Yang YS. Peritoneal cellular immunity and endometriosis. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1997;38:400–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

