SMN complex localizes to the sarcomeric Z-disc and is a proteolytic target of calpain
- PMID: 18689355
- PMCID: PMC2566527
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddn234
SMN complex localizes to the sarcomeric Z-disc and is a proteolytic target of calpain
Abstract
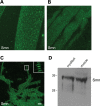
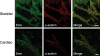
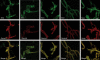
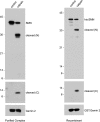
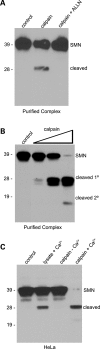
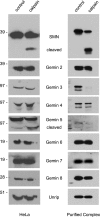
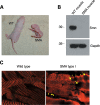
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a recessive neuromuscular disease caused by mutations in the human survival motor neuron 1 (SMN1) gene. The human SMN protein is part of a large macromolecular complex involved in the biogenesis of small ribonucleoproteins. Previously, we showed that SMN is a sarcomeric protein in flies and mice. In this report, we show that the entire mouse Smn complex localizes to the sarcomeric Z-disc. Smn colocalizes with alpha-actinin, a Z-disc marker protein, in both skeletal and cardiac myofibrils. Furthermore, this localization is both calcium- and calpain-dependent. Calpains are known to release proteins from various regions of the sarcomere as a part of the normal functioning of the muscle; however, this removal can be either direct or indirect. Using mammalian cell lysates, purified native SMN complexes, as well as recombinant SMN protein, we show that SMN is a direct target of calpain cleavage. Finally, myofibers from a mouse model of severe SMA, but not controls, display morphological defects that are consistent with a Z-disc deficiency. These results support the view that the SMN complex performs a muscle-specific function at the Z-discs.
Figures


References
-
- Wirth B., Brichta L., Hahnen E. Spinal muscular atrophy: from gene to therapy. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2006;13:121–131. - PubMed
-
- Kolb S.J., Battle D.J., Dreyfuss G. Molecular functions of the SMN complex. J. Child Neurol. 2007;22:990–994. - PubMed
-
- Sumner C.J. Molecular mechanisms of spinal muscular atrophy. J. Child Neurol. 2007;22:979–989. - PubMed
-
- Eggert C., Chari A., Laggerbauer B., Fischer U. Spinal muscular atrophy: the RNP connection. Trends Mol. Med. 2006;12:113–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

