Diffusional channeling in the sulfate-activating complex: combined continuum modeling and coarse-grained brownian dynamics studies
- PMID: 18689458
- PMCID: PMC2576392
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.108.140038
Diffusional channeling in the sulfate-activating complex: combined continuum modeling and coarse-grained brownian dynamics studies
Abstract
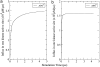
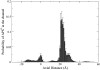
Enzymes required for sulfur metabolism have been suggested to gain efficiency by restricted diffusion (i.e., channeling) of an intermediate APS(2-) between active sites. This article describes modeling of the whole channeling process by numerical solution of the Smoluchowski diffusion equation, as well as by coarse-grained Brownian dynamics. The results suggest that electrostatics plays an essential role in the APS(2-) channeling. Furthermore, with coarse-grained Brownian dynamics, the substrate channeling process has been studied with reactions in multiple active sites. Our simulations provide a bridge for numerical modeling with Brownian dynamics to simulate the complicated reaction and diffusion and raise important questions relating to the electrostatically mediated substrate channeling in vitro, in situ, and in vivo.
Figures










References
-
- Huang, X. Y., H. M. Holden, and F. M. Raushel. 2001. Channeling of substrates and intermediates in enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70:149–180. - PubMed
-
- Miles, E. W., S. Rhee, and D. R. Davies. 1999. The molecular basis of substrate channeling. J. Biol. Chem. 274:12193–12196. - PubMed
-
- Ushiroyama, T., T. Fukushima, J. D. Styre, and H. O. Spivey. 1992. Substrate channeling of NADH in mitochondrial redox processes. Curr. Top. Cell. Regul. 33:291–307. - PubMed
-
- Rudolph, J., and J. Stubbe. 1995. Investigation of the mechanism of phosphoribosylamine transfer from glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase to glycinamide ribonucleotide synthetase. Biochemistry. 34:2241–2250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

