Comprehensive assessment of the regulons controlled by the FixLJ-FixK2-FixK1 cascade in Bradyrhizobium japonicum
- PMID: 18689489
- PMCID: PMC2566219
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00748-08
Comprehensive assessment of the regulons controlled by the FixLJ-FixK2-FixK1 cascade in Bradyrhizobium japonicum
Abstract
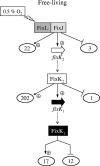
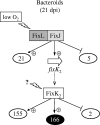
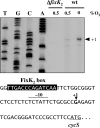
Symbiotic N(2) fixation in Bradyrhizobium japonicum is controlled by a complex transcription factor network. Part of it is a hierarchically arranged cascade in which the two-component regulatory system FixLJ, in response to a moderate decrease in oxygen concentration, activates the fixK(2) gene. The FixK(2) protein then activates not only a number of genes essential for microoxic respiration in symbiosis (fixNOQP and fixGHIS) but also further regulatory genes (rpoN(1), nnrR, and fixK(1)). The results of transcriptome analyses described here have led to a comprehensive and expanded definition of the FixJ, FixK(2), and FixK(1) regulons, which, respectively, consist of 26, 204, and 29 genes specifically regulated in microoxically grown cells. Most of these genes are subject to positive control. Particular attention was addressed to the FixK(2)-dependent genes, which included a bioinformatics search for putative FixK(2) binding sites on DNA (FixK(2) boxes). Using an in vitro transcription assay with RNA polymerase holoenzyme and purified FixK(2) as the activator, we validated as direct targets eight new genes. Interestingly, the adjacent but divergently oriented fixK(1) and cycS genes shared the same FixK(2) box for the activation of transcription in both directions. This recognition site may also be a direct target for the FixK(1) protein, because activation of the cycS promoter required an intact fixK(1) gene and either microoxic or anoxic, denitrifying conditions. We present evidence that cycS codes for a c-type cytochrome which is important, but not essential, for nitrate respiration. Two other, unexpected results emerged from this study: (i) specifically FixK(1) seemed to exert a negative control on genes that are normally activated by the N(2) fixation-specific transcription factor NifA, and (ii) a larger number of genes are expressed in a FixK(2)-dependent manner in endosymbiotic bacteroids than in culture-grown cells, pointing to a possible symbiosis-specific control.
Figures


References
-
- Alexeyev, M. F. 1995. Three kanamycin resistance gene cassettes with different polylinkers. BioTechniques 1852-56. - PubMed
-
- Anthamatten, D., and H. Hennecke. 1991. The regulatory status of the fixL- and fixJ-like genes in Bradyrhizobium japonicum may be different from that in Rhizobium meliloti. Mol. Gen. Genet. 22538-48. - PubMed
-
- Babst, M., H. Hennecke, and H. M. Fischer. 1996. Two different mechanisms are involved in the heat-shock regulation of chaperonin gene expression in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol. Microbiol. 19827-839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

