Inhibitor-2 prevents protein phosphatase 1-induced cardiac hypertrophy and mortality
- PMID: 18689497
- PMCID: PMC2593509
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00515.2008
Inhibitor-2 prevents protein phosphatase 1-induced cardiac hypertrophy and mortality
Abstract
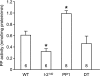
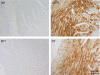
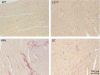
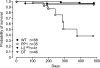
Cardiac-specific overexpression of the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase type 1 (PP1) in mice results in hypertrophy, depressed contractility, propensity to heart failure, and premature death. To further address the role of PP1 in heart function, PP1 mice were crossed with mice that overexpress a functional COOH-terminally truncated form of PP1 inhibitor-2 (I-2(140)). Protein phosphatase activity was increased in PP1 mice but was normalized in double transgenic (DT) mice. The maximal rates of contraction (+dP/dt) and of relaxation (-dP/dt) were reduced in catheterized PP1 mice but normalized in DT mice. Similar contractile abnormalities were observed in isolated, perfused work-performing hearts and in whole animals by means of echocardiography. The increased absolute and relative heart weights observed in PP1 mice were normalized in DT mice. Histological analyses indicated that PP1 mice had significant cardiac fibrosis, which was absent in DT mice. Furthermore, PP1 mice exhibited an age-dependent increase in mortality, which was abrogated in DT mice. These results indicate that I-2 overexpression prevents the detrimental effects of PP1 overexpression in the heart and further underscore the fundamental role of PP1 in cardiac function. Therefore, PP1 inhibitors such as I-2 could offer new therapeutic options to ameliorate the deleterious effects of heart failure.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enhanced cardiac function in mice overexpressing protein phosphatase Inhibitor-2.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Oct 1;68(1):98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.05.019. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15975567
-
Inhibition of protein phosphatase 1 by inhibitor-2 exacerbates progression of cardiac failure in a model with pressure overload.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Aug 1;79(3):464-71. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn113. Epub 2008 May 3. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18453636
-
Complex functionality of protein phosphatase 1 isoforms in the heart.Cell Signal. 2021 Sep;85:110059. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110059. Epub 2021 May 29. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 34062239 Review.
-
Inhibition of Na(+)-H(+) exchange prevents hypertrophy, fibrosis, and heart failure in beta(1)-adrenergic receptor transgenic mice.Circ Res. 2002 Apr 19;90(7):814-9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000014966.97486.c0. Circ Res. 2002. PMID: 11964375
-
Is IIIG9 a New Protein with Exclusive Ciliary Function? Analysis of Its Potential Role in Cancer and Other Pathologies.Cells. 2022 Oct 21;11(20):3327. doi: 10.3390/cells11203327. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291193 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitor 1 of Protein Phosphatase 1 Regulates Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II to Alleviate Oxidative Stress in Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Injury of Cardiomyocytes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Dec 7;2019:2193019. doi: 10.1155/2019/2193019. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31885777 Free PMC article.
-
Functions and therapeutic potential of protein phosphatase 1: Insights from mouse genetics.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Jan;1866(1):16-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.07.019. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30056088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful overexpression of wild-type inhibitor-2 of PP1 in cardiovascular cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018 Aug;391(8):859-873. doi: 10.1007/s00210-018-1515-3. Epub 2018 May 24. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29797049
-
Serine-threonine protein phosphatase regulation of Cx43 dephosphorylation in arrhythmogenic disorders.Cell Signal. 2021 Oct;86:110070. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110070. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 34217833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulating the regulator: Insights into the cardiac protein phosphatase 1 interactome.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Dec;101:165-172. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.09.009. Epub 2016 Sep 20. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27663175 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baba HA, Iwai T, Irlbeck M, Schmid KW, Zimmer HG. Differential effects of angiotensin II receptor blockade on pressure-induced left ventricular hypertrophy and fibrosis in rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31: 445–455, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Bartel S, Stein B, Eschenhagen T, Mende U, Neumann J, Schmitz W, Krause EG, Karczewski P, Scholz H. Protein phosphorylation in isolated trabeculae from nonfailing and failing human hearts. Mol Cell Biochem 157: 171–179, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Bodor GS, Oakeley AE, Allen PD, Crimmins DL, Ladenson JH, Anderson PA. Troponin I phosphorylation in the normal and failing adult human heart. Circulation 96: 1495–1500, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Boknik P, Fockenbrock M, Herzig S, Knapp J, Linck B, Lüss H, Müller FU, Müller T, Schmitz W, Schröder F, Neumann J. Protein phosphatase activity is increased in a rat model of long-term β-adrenergic stimulation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 262: 222–231, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Brandt H, Lee EYC, Killilea SD. A protein inhibitor of rabbit liver phosphorylase phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 63: 950–956, 1975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

