Leptin-induced endothelial dysfunction in obesity
- PMID: 18689498
- PMCID: PMC2593507
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00479.2008
Leptin-induced endothelial dysfunction in obesity
Abstract
Hyperleptinemia accompanying obesity affects endothelial nitric oxide (NO) and is a serious factor for vascular disorders. NO, superoxide (O(2)(-)), and peroxynitrite (ONOO(-)) nanosensors were placed near the surface (5+/-2 microm) of a single human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) exposed to leptin or aortic endothelium of obese C57BL/6J mice, and concentrations of calcium ionophore (CaI)-stimulated NO, O(2)(-), ONOO(-) were recorded. Endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) expression and L-arginine concentrations in HUVEC and aortic endothelium were measured. Leptin did not directly stimulate NO, O(2)(-), or ONOO(-) release from HUVEC. However, a 12-h exposure of HUVEC to leptin increased eNOS expression and CaI-stimulated NO (625+/-30 vs. 500+/-24 nmol/l control) and dramatically increased cytotoxic O(2)(-) and ONOO(-) levels. The [NO]-to-[ONOO(-)] ratio ([NO]/[ONOO(-)]) decreased from 2.0+/-0.1 in normal to 1.30+/-0.1 in leptin-induced dysfunctional endothelium. In obese mice, a 2.5-fold increase in leptin concentration coincided with 100% increase in eNOS and about 30% decrease in intracellular L-arginine. The increased eNOS expression and a reduced l-arginine content led to eNOS uncoupling, a reduction in bioavailable NO (250+/-10 vs. 420+/-12 nmol/l control), and an elevated concentration of O(2)(-) (240%) and ONOO(-) (70%). L-Arginine and sepiapterin supplementation reversed eNOS uncoupling and partially restored [NO]/[ONOO(-)] balance in obese mice. In obesity, leptin increases eNOS expression and decreases intracellular l-arginine, resulting in eNOS an uncoupling and depletion of endothelial NO and an increase of cytotoxic ONOO(-). Hyperleptinemia triggers an endothelial NO/ONOO(-) imbalance characteristic of dysfunctional endothelium observed in other vascular disorders, i.e., atherosclerosis and diabetes.
Figures
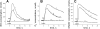
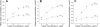
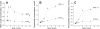
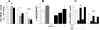



Similar articles
-
Adverse balance of nitric oxide/peroxynitrite in the dysfunctional endothelium can be reversed by statins.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007 Oct;50(4):391-8. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e31811f3fd0. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 18049306
-
Anti-atherogenic effect of statins: role of nitric oxide, peroxynitrite and haem oxygenase-1.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Apr;156(8):1256-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00125.x. Epub 2009 Feb 18. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19226281 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedical studies of the restoration of nitric oxide/peroxynitrite balance in dysfunctional endothelium by 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 - clinical implications for cardiovascular diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Jan 19;13:455-466. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S152822. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29416330 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: from marvel to menace.Circulation. 2006 Apr 4;113(13):1708-14. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.602532. Circulation. 2006. PMID: 16585403 Review.
-
Tackling endothelial dysfunction by modulating NOS uncoupling: new insights into its pathogenesis and therapeutic possibilities.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Mar 1;302(5):E481-95. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00540.2011. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22167522 Review.
Cited by
-
Isomer-specific effects of CLA on gene expression in human adipose tissue depending on PPARgamma2 P12A polymorphism: a double blind, randomized, controlled cross-over study.Lipids Health Dis. 2009 Aug 18;8:35. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-8-35. Lipids Health Dis. 2009. PMID: 19689798 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Early stage of obesity potentiates nitric oxide reduction during the development of renal failure.J Nephrol. 2014 Jun;27(3):281-7. doi: 10.1007/s40620-013-0029-9. Epub 2014 Jan 21. J Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24446346
-
Adipose tissue and vascular phenotypic modulation by voluntary physical activity and dietary restriction in obese insulin-resistant OLETF rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014 Apr 15;306(8):R596-606. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00493.2013. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24523340 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity retards the progression of diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice.Kidney Int. 2012 Dec;82(11):1176-83. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.248. Epub 2012 Jul 11. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22785174 Free PMC article.
-
Benefit of a low-fat over high-fat diet on vascular health during alternate day fasting.Nutr Diabetes. 2013 May 27;3(5):e71. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2013.14. Nutr Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23712283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agata J, Masuda A, Takada M, Higashiura K, Murakami H, Miyazaki Y, Shimamoto K. High plasma immunoreactive leptin level in essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 10: 1171–1174, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Beckman JS, Chen J, Ischiropoulos H, Crow JP. Oxidative chemistry of peroxynitrite. In: Methods in Enzymology, edited by Packer L. San Diego, CA: Academic, 1994, p. 229–240. - PubMed
-
- Beltowski J, Wojcicka G, Borkowska E. Human leptin stimulates systemic nitric oxide production in the rat. Obes Res 10: 939–946, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Bouloumié A, Drexler HC, Lafontan M, Busse R. Leptin, the product of Ob gene, promotes angiogenesis. Circ Res 83: 1059–1066, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Bouloumié A, Marumo T, Lafontan M, Busse R. Leptin induces oxidative stress in human endothelial cells. FASEB J 13: 1231–1238, 1999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

