Perinatal loss of Nkx2-5 results in rapid conduction and contraction defects
- PMID: 18689573
- PMCID: PMC2590500
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.171835
Perinatal loss of Nkx2-5 results in rapid conduction and contraction defects
Abstract
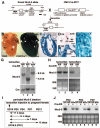
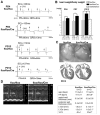
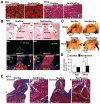
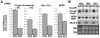
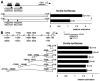
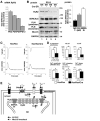
Homeobox transcription factor Nkx2-5, highly expressed in heart, is a critical factor during early embryonic cardiac development. In this study, using tamoxifen-inducible Nkx2-5 knockout mice, we demonstrate the role of Nkx2-5 in conduction and contraction in neonates within 4 days after perinatal tamoxifen injection. Conduction defect was accompanied by reduction in ventricular expression of the cardiac voltage-gated Na+ channel pore-forming alpha-subunit (Na(v)1.5-alpha), the largest ion channel in the heart responsive for rapid depolarization of the action potential, which leads to increased intracellular Ca2+ for contraction (conduction-contraction coupling). In addition, expression of ryanodine receptor 2, through which Ca2+ is released from sarcoplasmic reticulum, was substantially reduced in Nkx2-5 knockout mice. These results indicate that Nkx2-5 function is critical not only during cardiac development but also in perinatal hearts, by regulating expression of several important gene products involved in conduction and contraction.
Figures

References
-
- Bers DM. Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 2002;415:198–205. - PubMed
-
- Marban E. Cardiac channelopathies. Nature. 2002;415:213–218. - PubMed
-
- Mangoni ME, Couette B, Marger L, Bourinet E, Striessnig J, Nargeot J. Voltage-dependent calcium channels and cardiac pacemaker activity: from ionic currents to genes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2006;90:38–63. - PubMed
-
- Haufe V, Chamberland C, Dumaine R. The promiscuous nature of the cardiac sodium current. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;42:469–477. - PubMed
-
- Abriel H. Roles and regulation of the cardiac sodium channel Na(v) 1.5: recent insights from experimental studies. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;76:381–389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

