Magnitude-dependent effects of cyclic stretch on HGF- and VEGF-induced pulmonary endothelial remodeling and barrier regulation
- PMID: 18689603
- PMCID: PMC2575947
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.90236.2008
Magnitude-dependent effects of cyclic stretch on HGF- and VEGF-induced pulmonary endothelial remodeling and barrier regulation
Abstract
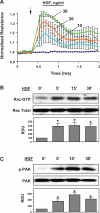
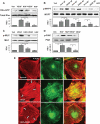
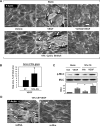
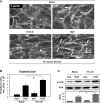
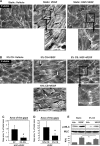
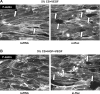
Mechanical ventilation at high tidal volumes compromises the blood-gas barrier and increases lung vascular permeability, which may lead to ventilator-induced lung injury and pulmonary edema. Using pulmonary endothelial cell (ECs) exposed to physiologically [5% cyclic stretch (CS)] and pathologically (18% CS) relevant magnitudes of CS, we evaluated the potential protective effects of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) on EC barrier dysfunction induced by CS and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). In static culture, HGF enhanced EC barrier function in a Rac-dependent manner and attenuated VEGF-induced EC permeability and paracellular gap formation. The protective effects of HGF were associated with the suppression of Rho-dependent signaling triggered by VEGF. Five percent CS promoted HGF-induced enhancement of the cortical F-actin rim and activation of Rac-dependent signaling, suggesting synergistic barrier-protective effects of physiological CS and HGF. In contrast, 18% CS further enhanced VEGF-induced EC permeability, activation of Rho signaling, and formation of actin stress fibers and paracellular gaps. These effects were attenuated by HGF pretreatment. EC preconditioning at 5% CS before HGF and VEGF further promoted EC barrier maintenance. Our data suggest synergistic effects of HGF and physiological CS in the Rac-mediated mechanisms of EC barrier protection. In turn, HGF reduced the barrier-disruptive effects of VEGF and pathological CS via downregulation of the Rho pathway. These results support the importance of HGF-VEGF balance in control of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome severity via small GTPase-dependent regulation of lung endothelial permeability.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HGF attenuates thrombin-induced endothelial permeability by Tiam1-mediated activation of the Rac pathway and by Tiam1/Rac-dependent inhibition of the Rho pathway.FASEB J. 2007 Sep;21(11):2776-86. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-7660com. Epub 2007 Apr 11. FASEB J. 2007. PMID: 17428964
-
Paxillin is involved in the differential regulation of endothelial barrier by HGF and VEGF.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009 Jan;40(1):99-107. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0099OC. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 18664639 Free PMC article.
-
Role of End Binding Protein-1 in endothelial permeability response to barrier-disruptive and barrier-enhancing agonists.Cell Signal. 2017 Jan;29:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.09.005. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Cell Signal. 2017. PMID: 27667566 Free PMC article.
-
Rho GTPases and the regulation of endothelial permeability.Vascul Pharmacol. 2002 Nov;39(4-5):187-99. doi: 10.1016/s1537-1891(03)00008-9. Vascul Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12747959 Review.
-
Driving Rho GTPase activity in endothelial cells regulates barrier integrity.Thromb Haemost. 2010 Jan;103(1):40-55. doi: 10.1160/TH09-06-0403. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Thromb Haemost. 2010. PMID: 20062930 Review.
Cited by
-
Angiogenesis: Biological Mechanisms and In Vitro Models.Ann Biomed Eng. 2025 Jul;53(7):1543-1574. doi: 10.1007/s10439-025-03721-2. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Ann Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 40210793 Review.
-
Modulation of Endothelial Inflammation by Low and High Magnitude Cyclic Stretch.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 29;11(4):e0153387. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153387. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27128976 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule dynamics control HGF-induced lung endothelial barrier enhancement.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 8;9(9):e105912. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105912. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25198505 Free PMC article.
-
Synergism of MSC-secreted HGF and VEGF in stabilising endothelial barrier function upon lipopolysaccharide stimulation via the Rac1 pathway.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Dec 16;6:250. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0257-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26674641 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells regulate the Th17/Treg cell balance partly through hepatocyte growth factor in vitro.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Feb 28;11(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01612-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32111238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aird WC Endothelial cell heterogeneity. Crit Care Med 31: S221–230, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Aoki M, Morishita R, Taniyama Y, Kaneda Y, Ogihara T. Therapeutic angiogenesis induced by hepatocyte growth factor: potential gene therapy for ischemic diseases. J Atheroscler Thromb 7: 71–76, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Becker PM, Verin AD, Booth MA, Liu F, Birukova A, Garcia JG. Differential regulation of diverse physiological responses to VEGF in pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 281: L1500–L1511, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Bhullar IS, Li YS, Miao H, Zandi E, Kim M, Shyy JY, Chien S. Fluid shear stress activation of IkappaB kinase is integrin-dependent. J Biol Chem 273: 30544–30549, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Birukov KG, Birukova AA, Dudek SM, Verin AD, Crow MT, Zhan X, DePaola N, Garcia JG. Shear stress-mediated cytoskeletal remodeling and cortactin translocation in pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 26: 453–464, 2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

