In vivo assessment of pyruvate dehydrogenase flux in the heart using hyperpolarized carbon-13 magnetic resonance
- PMID: 18689683
- PMCID: PMC2515222
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0805953105
In vivo assessment of pyruvate dehydrogenase flux in the heart using hyperpolarized carbon-13 magnetic resonance
Abstract
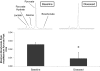
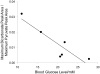
The advent of hyperpolarized (13)C magnetic resonance (MR) has provided new potential for the real-time visualization of in vivo metabolic processes. The aim of this work was to use hyperpolarized [1-(13)C]pyruvate as a metabolic tracer to assess noninvasively the flux through the mitochondrial enzyme complex pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) in the rat heart, by measuring the production of bicarbonate (H(13)CO(3)(-)), a byproduct of the PDH-catalyzed conversion of [1-(13)C]pyruvate to acetyl-CoA. By noninvasively observing a 74% decrease in H(13)CO(3)(-) production in fasted rats compared with fed controls, we have demonstrated that hyperpolarized (13)C MR is sensitive to physiological perturbations in PDH flux. Further, we evaluated the ability of the hyperpolarized (13)C MR technique to monitor disease progression by examining PDH flux before and 5 days after streptozotocin induction of type 1 diabetes. We detected decreased H(13)CO(3)(-) production with the onset of diabetes that correlated with disease severity. These observations were supported by in vitro investigations of PDH activity as reported in the literature and provided evidence that flux through the PDH enzyme complex can be monitored noninvasively, in vivo, by using hyperpolarized (13)C MR.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Grant funding from GE Healthcare.
Figures


References
-
- Stanley WC, Recchia FA, Lopaschuk GD. Myocardial substrate metabolism in the normal and failing heart. Physiol Rev. 2005;85:1093–1129. - PubMed
-
- Taegtmeyer H, McNulty P, Young ME. Adaptation and maladaptation of the heart in diabetes. I. General concepts. Circulation. 2002;105:1727–1733. - PubMed
-
- Randle PJ. Fuel selection in animals. Biochem Soc Trans. 1986;14:799–806. - PubMed
-
- Randle PJ, Garland PB, Hales CN, Newsholme EA. The glucose fatty-acid cycle: Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1963;1:785–789. - PubMed
-
- Reed LJ. Regulation of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by a phosphorylation–dephosphorylation cycle. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;18:95–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

