Glycan microarray of Globo H and related structures for quantitative analysis of breast cancer
- PMID: 18689688
- PMCID: PMC2575271
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0804923105
Glycan microarray of Globo H and related structures for quantitative analysis of breast cancer
Abstract
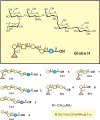
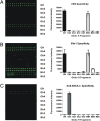
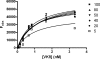
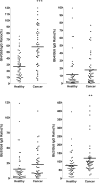
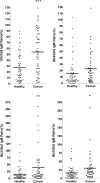
Cancer-associated carbohydrate antigens are often found on the surface of cancer cells. Understanding their roles in cancer progression will lead to the development of new therapeutics and high-sensitivity diagnostics for cancers. Globo H is a member of this family, which is highly expressed on breast cancer cells. Here, we report the development of a glycan microarray of Globo H and its analogs for measurement of the dissociation constants on surface (K(D,surf)) with three different monoclonal antibodies (VK-9, Mbr1, and anti-SSEA-3), to deduce their binding specificity. The glycan microarray was also used to detect the amount of antibodies present in the plasma of breast cancer patients and normal blood donors. It was shown that the amount of antibodies against Globo H from breast cancer patients were significantly higher than normal blood donors, providing a new tool for possible breast cancer diagnosis. Compared with the traditional ELISA method, this array method required only atto-mole amounts of materials and is more effective and more sensitive (5 orders of magnitude). The glycan microarray thus provides a new platform for use to monitor the immune response to carbohydrate epitopes after vaccine therapy or during the course of cancer progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
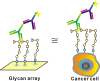
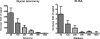
Similar articles
-
Carbohydrate microarray for profiling the antibodies interacting with Globo H tumor antigen.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jan 3;103(1):15-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509693102. Epub 2005 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16373501 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally occurring anti-glycan antibodies binding to Globo H-expressing cells identify ovarian cancer patients.J Ovarian Res. 2017 Feb 10;10(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13048-017-0305-8. J Ovarian Res. 2017. PMID: 28187738 Free PMC article.
-
New development of glycan arrays.Org Biomol Chem. 2009 Jun 7;7(11):2247-54. doi: 10.1039/b902510n. Epub 2009 Apr 27. Org Biomol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19462030
-
Tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens defining tumor malignancy: basis for development of anti-cancer vaccines.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001;491:369-402. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-1267-7_24. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001. PMID: 14533809 Review.
-
Application of microarrays for deciphering the structure and function of the human glycome.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Apr;12(4):902-12. doi: 10.1074/mcp.R112.027110. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23412570 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Globo H ceramide is an independent prognostic marker for gallbladder cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Oct 15;13(10):4811-4821. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37970342 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-associated glycans and their role in gynecological cancers: accelerating translational research by novel high-throughput approaches.Metabolites. 2012 Nov 14;2(4):913-39. doi: 10.3390/metabo2040913. Metabolites. 2012. PMID: 24957768 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative glycomics from fluidic glycan microarrays.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Sep 30;131(38):13646-50. doi: 10.1021/ja902783n. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19731906 Free PMC article.
-
Serum antibody screening using glycan arrays.Chem Soc Rev. 2024 Mar 4;53(5):2603-2642. doi: 10.1039/d3cs00693j. Chem Soc Rev. 2024. PMID: 38305761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunization of fucose-containing polysaccharides from Reishi mushroom induces antibodies to tumor-associated Globo H-series epitopes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 20;110(34):13809-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312457110. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23908400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kannagi R, et al. New globo series glycospingolipids in human tetraocarcinoma reactive with the monoclonal-antibody directed to a developmentally regulated antigen, stage-specific embryonic antigen-3. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:8934–8942. - PubMed
-
- Zhang SL, et al. Selection of tumor antigens as targets for immune attack using immunohistochemistry. 1. Focus on gangliosides. Int J Cancer. 1997;73:42–49. - PubMed
-
- Hakomori S, Zhang YM. Glycosphingolipid antigens and cancer therapy. Chem Biol. 1997;4:97–104. - PubMed
-
- Dube DH, Bertozzi CR. Glycans in cancer and inflammation. Potential for therapeutics and diagnostics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:477–488. - PubMed
-
- Menard S, Tagliabue E, Canevari S, Fossati G, Colnaghi MI. Generation of monoclonal-antibodies reacting with normal and cancer-cells of human-breast. Cancer Res. 1983;43:1295–1300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

