Focused glycomic analysis of the N-linked glycan biosynthetic pathway in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 18690643
- PMCID: PMC3970323
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.200800157
Focused glycomic analysis of the N-linked glycan biosynthetic pathway in ovarian cancer
Abstract
Epithelial ovarian cancer is the deadliest female reproductive tract malignancy in Western countries. Less than 25% of cases are diagnosed when the cancer is confined, however, pointing to the critical need for early diagnostics for ovarian cancer. Identifying the changes that occur in the glycome of ovarian cancer cells may provide an avenue to develop a new generation of potential biomarkers for early detection of this disease. We performed a glycotranscriptomic analysis of endometrioid ovarian carcinoma using human tissue, as well as a newly developed mouse model that mimics this disease. Our results show that the N-linked glycans expressed in both nondiseased mouse and human ovarian tissues are similar; moreover, malignant changes in the expression of N-linked glycans in both mouse and human endometrioid ovarian carcinoma are qualitatively similar. Lectin reactivity was used as a means for rapid validation of glycan structural changes in the carcinomas that were predicted by the glycotranscriptome analysis. Among several changes in glycan expression noted, the increase of bisected N-linked glycans and the transcripts of the enzyme responsible for its biosynthesis, GnT-III, was the most significant. This study provides evidence that glycotranscriptome analysis can be an important tool in identifying potential cancer biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

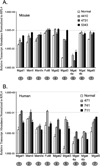

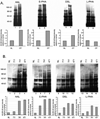
References
-
- Pierce M, Arango J. Rous sarcoma virus-transformed baby hamster kidney cells express higher levels of asparagine-linked tri- and tetraantennary glycopeptides containing [GlcNAc-beta (1,6)Man-alpha (1,6)Man] and poly-N-acetyllactosamine sequences than baby hamster kidney cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1986;261:10772–10777. - PubMed
-
- Meezan E, Wu HC, Black PH, Robbins PW. Comparative studies on the carbohydrate-containing membrane components of normal and virus-transformed mouse fibroblasts. II. Separation of glycoproteins and glycopeptides by sephadex chromatography. Biochemistry. 1969;8:2518–2524. - PubMed
-
- Guo HB, Lee I, Kamar M, Akiyama SK, Pierce M. Aberrant N-glycosylation of beta1 integrin causes reduced alpha5beta1 integrin clustering and stimulates cell migration. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6837–6845. - PubMed
-
- Guo HB, Lee I, Kamar M, Pierce M. N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V expression levels regulate cad-herin-associated homotypic cell–cell adhesion and intracellular signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:52412–52424. - PubMed
-
- Guo HB, Randolph M, Pierce M. Inhibition of a specific N-glycosylation activity results in attenuation of breast carcinoma cell invasiveness-related phenotypes: inhibition of epidermal growth factor-induced dephosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:22150–22162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

