Clinico-pathologic function of cerebral ABC transporters - implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 18690837
- PMCID: PMC2753594
- DOI: 10.2174/156720508785132262
Clinico-pathologic function of cerebral ABC transporters - implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
In recent years it has become evident that ABC transporters fulfill important barrier functions in normal organs and during disease processes. Most importantly, resistance to drugs in cancer cells led to intense oncological and pharmacological investigations in which researchers were able to highlight important pharmacological interactions of chemotherapeuticals with ABC transporter function. Recently, the development of neurodegenerative diseases and the maintenance of neuronal stem cells have been linked to the activity of ABC transporters. Here, we summarize findings from cell culture experiments, animal models and studies of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Furthermore, we discuss pharmacological interactions and computational methods for risk assessment.
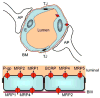
Figures


References
-
- Linton KJ. Structure and function of ABC transporters. Physiology (Bethesda) 2007;22:122–30. - PubMed
-
- Schinkel AH, Jonker JW. Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family: an overview. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55:3–29. - PubMed
-
- Islam MO, Kanemura Y, Tajria J, et al. Functional expression of ABCG2 transporter in human neural stem/progenitor cells. Neurosci Res. 2005;52:75–82. - PubMed
-
- Broccardo C, Nieoullon V, Amin R, et al. ABCA2 is a marker of neural progenitors and neuronal subsets in the adult rodent brain. J Neurochem. 2006;97:345–55. - PubMed
-
- Islam MO, Kanemura Y, Tajria J, et al. Characterization of ABC transporter ABCB1 expressed in human neural stem/progenitor cells. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:3473–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

