Neuroprotection in stroke by complement inhibition and immunoglobulin therapy
- PMID: 18691639
- PMCID: PMC2639633
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.07.015
Neuroprotection in stroke by complement inhibition and immunoglobulin therapy
Abstract
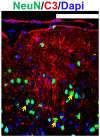
Activation of the complement system occurs in a variety of neuroinflammatory diseases and neurodegenerative processes of the CNS. Studies in the last decade have demonstrated that essentially all of the activation components and receptors of the complement system are produced by astrocytes, microglia, and neurons. There is also rapidly growing evidence to indicate an active role of the complement system in cerebral ischemic injury. In addition to direct cell damage, regional cerebral ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) induces an inflammatory response involving complement activation and generation of active fragments, such as C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins, C3b, C4b, and iC3b. The use of specific inhibitors to block complement activation or their mediators such as C5a, can reduce local tissue injury after I/R. Consistent with therapeutic approaches that have been successful in models of autoimmune disorders, many of the same complement inhibition strategies are proving effective in animal models of cerebral I/R injury. One new form of therapy, which is less specific in its targeting of complement than monodrug administration, is the use of immunoglobulins. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) has the potential to inhibit multiple components of inflammation, including complement fragments, pro-inflammatory cytokine production and leukocyte cell adhesion. Thus, IVIG may directly protect neurons, reduce activation of intrinsic inflammatory cells (microglia) and inhibit transendothelial infiltration of leukocytes into the brain parenchyma following an ischemic stroke. The striking neuroprotective actions of IVIG in animal models of ischemic stroke suggest a potential therapeutic potential that merits consideration for clinical trials in stroke patients.
Figures
References
-
- Ames RS, Li Y, Sarau HM, Nuthulaganti P, Foley JJ, Ellis C, Zeng Z, Su K, Jurewicz AJ, Hertzberg RP, Bergsma DJ, Kumar C. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human anaphylatoxin C3a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20231–20234. - PubMed
-
- Akita N, Nakase H, Kaido T, Kanemoto Y, Sakaki T. Protective effect of C1 esterase inhibitor on reperfusion injury in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Neurosurgery. 2003;52:395–400. - PubMed
-
- Ames RS, Lee D, Foley JJ, Jurewicz AJ, Tornetta MA, Bautsch W, Settmacher B, Klos A, Erhard KF, Cousins RD, Sulpizio AC, Hieble JP, McCafferty G, Ward KW, Adams JL, Bondinell WE, Underwood DC, Osborn RR, Badger AM, Sarau HM. Identification of a selective nonpeptide antagonist of the anaphylatoxin C3a receptor that demonstrates antiinflammatory activity in animal models. J Immunol. 2001;166:6341–6348. - PubMed
-
- Amzel LM, Poljak RJ. Three-dimensional structure of immunoglobulins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:961–997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

