T cell-specific siRNA delivery suppresses HIV-1 infection in humanized mice
- PMID: 18691745
- PMCID: PMC2943428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.06.034
T cell-specific siRNA delivery suppresses HIV-1 infection in humanized mice
Abstract
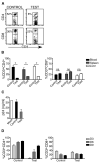
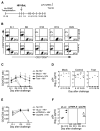
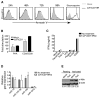
Evaluation of the therapeutic potential of RNAi for HIV infection has been hampered by the challenges of siRNA delivery and lack of suitable animal models. Using a delivery method for T cells, we show that siRNA treatment can dramatically suppress HIV infection. A CD7-specific single-chain antibody was conjugated to oligo-9-arginine peptide (scFvCD7-9R) for T cell-specific siRNA delivery in NOD/SCIDIL2rgamma-/- mice reconstituted with human lymphocytes (Hu-PBL) or CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells (Hu-HSC). In HIV-infected Hu-PBL mice, treatment with anti-CCR5 (viral coreceptor) and antiviral siRNAs complexed to scFvCD7-9R controlled viral replication and prevented the disease-associated CD4 T cell loss. This treatment also suppressed endogenous virus and restored CD4 T cell counts in mice reconstituted with HIV+ peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Moreover, scFvCD7-9R could deliver antiviral siRNAs to naive T cells in Hu-HSC mice and effectively suppress viremia in infected mice. Thus, siRNA therapy for HIV infection appears to be feasible in a preclinical animal model.
Figures



Comment in
-
Silencing HIV-1 In Vivo.Cell. 2008 Aug 22;134(4):566-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.004. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18724929
References
-
- Anderson J, Li MJ, Palmer B, Remling L, Li S, Yam P, Yee JK, Rossi J, Zaia J, Akkina R. Safety and efficacy of a lentiviral vector containing three anti-HIV genes--CCR5 ribozyme, tat-rev siRNA, and TAR decoy--in SCID-hu mouse-derived T cells. Mol Ther. 2007;15:1182–1188. - PubMed
-
- Banerjea A, Li MJ, Bauer G, Remling L, Lee NS, Rossi J, Akkina R. Inhibition of HIV-1 by Lentiviral Vector-Transduced siRNAs in T Lymphocytes Differentiated in SCID-hu Mice and CD34+ Progenitor Cell-Derived Macrophages. Mol Ther. 2003;8:62–71. - PubMed
-
- Bonilla FA, Kokron CM, Swinton P, Geha RS. Targeted gene disruption of murine CD7. Int Immunol. 1997;9:1875–1883. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

