Molecular inflammation: underpinnings of aging and age-related diseases
- PMID: 18692159
- PMCID: PMC3782993
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2008.07.002
Molecular inflammation: underpinnings of aging and age-related diseases
Abstract
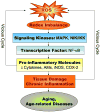
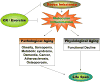
Recent scientific studies have advanced the notion of chronic inflammation as a major risk factor underlying aging and age-related diseases. In this review, low-grade, unresolved, molecular inflammation is described as an underlying mechanism of aging and age-related diseases, which may serve as a bridge between normal aging and age-related pathological processes. Accumulated data strongly suggest that continuous (chronic) upregulation of pro-inflammatory mediators (e.g., TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6, COX-2, iNOS) are induced during the aging process due to an age-related redox imbalance that activates many pro-inflammatory signaling pathways, including the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. These pro-inflammatory molecular events are discussed in relation to their role as basic mechanisms underlying aging and age-related diseases. Further, the anti-inflammatory actions of aging-retarding caloric restriction and exercise are reviewed. Thus, the purpose of this review is to describe the molecular roles of age-related physiological functional declines and the accompanying chronic diseases associated with aging. This new view on the role of molecular inflammation as a mechanism of aging and age-related pathogenesis can provide insights into potential interventions that may affect the aging process and reduce age-related diseases, thereby promoting healthy longevity.
Figures
References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Sethi G, Ahn KS, Sandur SK, Pandey MK, Kunnumakkara AB, Sung B, Ichikawa H. Targeting signal-transducer-and-activator-of-transcription-3 for prevention and therapy of cancer: modern target but ancient solution. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2006;1091:151–169. - PubMed
-
- Aigner T, Söder S, Gebhard PM, McAlinden A, Haag J. Mechanisms of disease: role of chondrocytes in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis--structure, chaos and senescence. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007;3:391–399. - PubMed
-
- Alamanos Y, Voulgari PV, Drosos AA. Incidence and prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis, based on the 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006;36:182–188. - PubMed
-
- Anker SD, Ponikowski PP, Clark AL, Leyva F, Rauchhaus M, Kemp M. Cytokines and neurohormones relating to body composition alterations in the wasting syndrome of chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 1999;20:683–693. - PubMed
-
- Arvin B, Neville LF, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ. The role of inflammation and cytokines in brain injury. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1996;20:445–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

